About Sudan
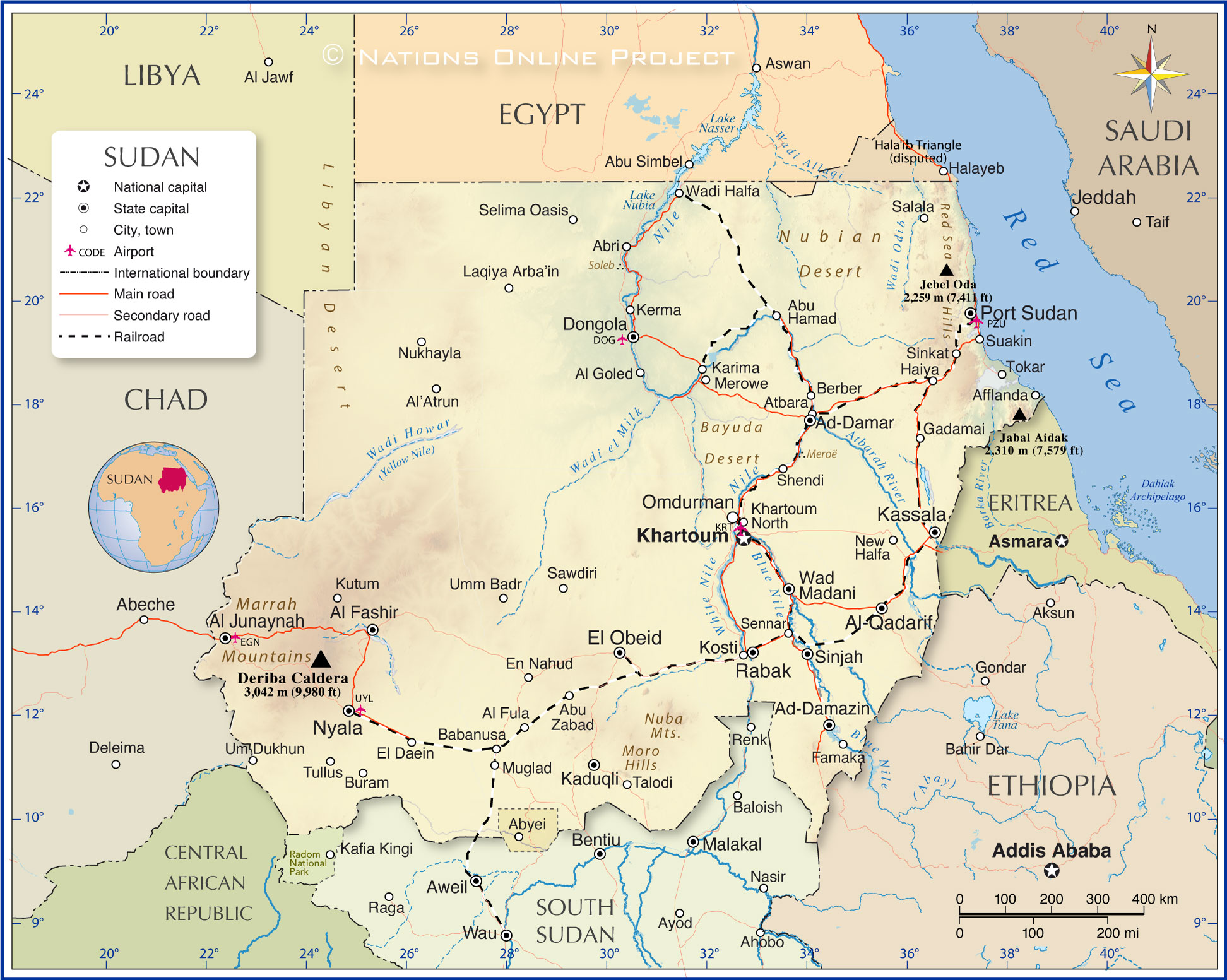
The map shows Sudan, formerly Africa's largest country by land area. The country split into two parts in 2011.
Sudan, officially the Republic of the Sudan, with a predominantly Arab population and
South Sudan, officially the Republic of South Sudan, with a population of about 8 million people of mainly African ethnic origin (Dinka, Nuer, Karo and other Nilotic tribes). Before the partition, South Sudan was an autonomous region in Sudan.
In January 2011, Southern Sudan held an independence referendum on whether the region should remain a part of Sudan or become independent. An overwhelming majority of almost 99% voted in favor of independence. The capital of South Sudan is
Juba.
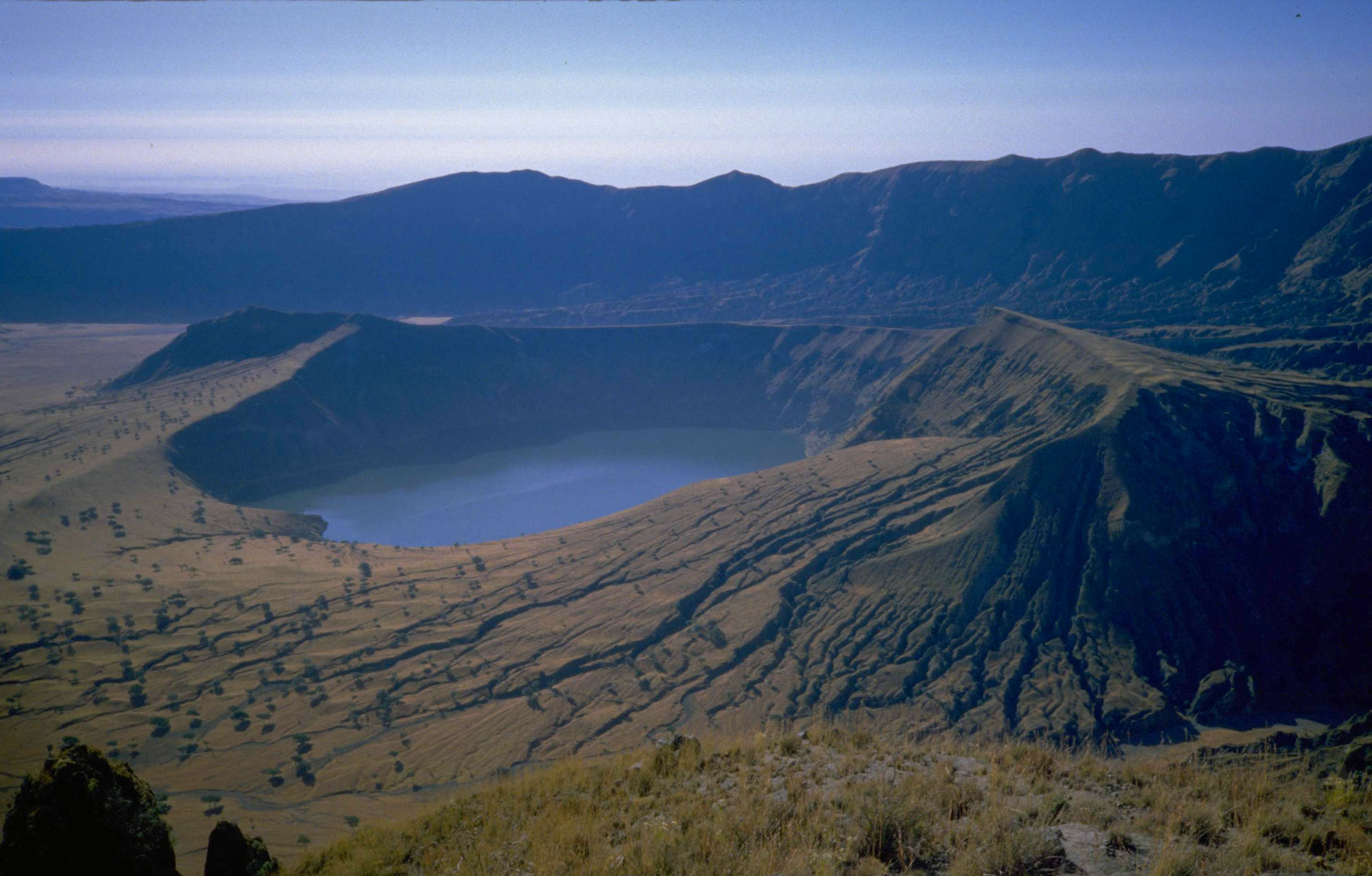 Sudan's highest point is the Deriba Caldera at (3042 meters/9,980 feet). The collapsed volcano is part of the Jebel Marra massif, a range of volcanic peaks in the southwest of the country.
Image: Hammy07
Sudan's highest point is the Deriba Caldera at (3042 meters/9,980 feet). The collapsed volcano is part of the Jebel Marra massif, a range of volcanic peaks in the southwest of the country.
Image: Hammy07
The Republic of the Sudan is located between
Egypt and
Eritrea in northeastern Africa, bordering the
Red Sea in the northeast.
It borders
Libya in the northwest,
Chad in the west, the
Central African Republic in the southwest, South Sudan in the south, and
Ethiopia in the southeast.
With an
area of 1,886,068 km², Sudan is the 16th largest country in the world; compared, it is more than five times the size of
Germany or slightly less than three times the size of
Texas.
Basically, the country consists of a vast plain bordered on three sides by mountains; to the northeast by the
Red Sea Hills, the hills separate the narrow coastal plain from the Eastern Desert (aka the Nubian Desert). In the south are the
Nuba Mountains and the Moro Hills, and in the southwest of the country are the
Marrah Mountains, with
Deriba Caldera (3,042 m/9,980 ft) as the highest peak. Deserts dominate the north.
See also:
 Topographic Map of Sudan
Topographic Map of Sudan.
Sudan has a
population of 46 million people (in 2022; the capital city is
Khartoum, the largest city is
Omdurman and Sudan's chief port is
Port Sudan. The predominant
language in the country is Sudanese Arabic; Beja (Bedawi), a Cushitic language, is spoken along the Red Sea.
The principal airports of Sudan are
Khartoum International Airport (
IATA code: KRT) and
Port Sudan New International Airport (IATA code: PZU) in Port Sudan; regional airports are in Dongola, Al Junaynah (Geneina Airport, IATA code: EGN) and Nyala (IATA: UYL).
More about Sudan
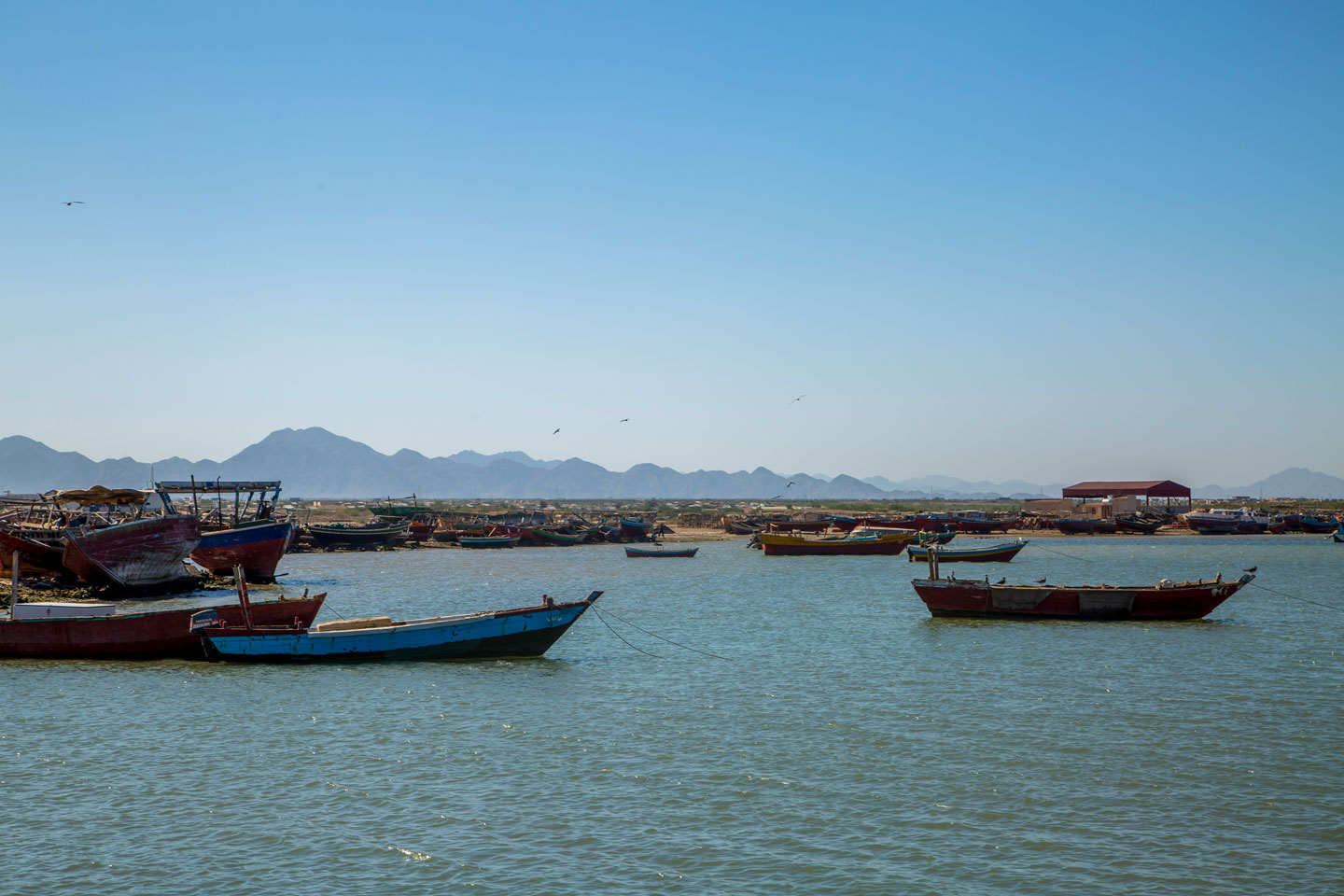 Fishing boats in the Red Sea, the Red Sea Hills in the background.
Photo: Mohammed
Fishing boats in the Red Sea, the Red Sea Hills in the background.
Photo: Mohammed
Sudan gained independence from British and Egyptian colonial rule in 1956.
In July 2011, Sudan was divided into two countries after the people of the south voted for independence. South Sudan became an independent state on 9th July 2011.
The division was a result of a long-standing conflict between the north and south of Sudan.
The conflict was mainly due to differences in religion, ethnicity, and political power. In the north, the population is predominantly Muslim and Arab, while in the south, people are predominantly of African descent and Christian. The division led to the displacement of millions of people and caused a humanitarian crisis.
Geography of Sudan
Sudan is one of the most geographically diverse countries in Africa. Its landscape includes the
Sahara Desert in the north, the coast of the
Red Sea in the northwest, the plains and plateaus of the semi-arid
Sahel zone in the center, mountains in the northeast and southwest, and the East Sudanian savanna and rainforests in the south. The central and southern parts of Sudan have different rainy seasons depending on latitude.
Sudan's lifeline is the
Nile River. The Nile is formed north of Khartoum by the confluence of its two main tributaries, the White Nile and the Blue Nile.
Climate
The largest part of the country has a warm desert climate (BWh). The southern part is in a semi-arid climate zone (BSh), except for two small regions, one in southern Darfur and one in Blue Nile State, with a tropical savanna climate (Aw). Rainfall in Sudan is unreliable and erratic, with large differences between northern and southern regions. The average annual temperatures range from 26°C to 32°C, with summer temperatures often exceeding 40°C in the north.
Sudan Administrative Divisions
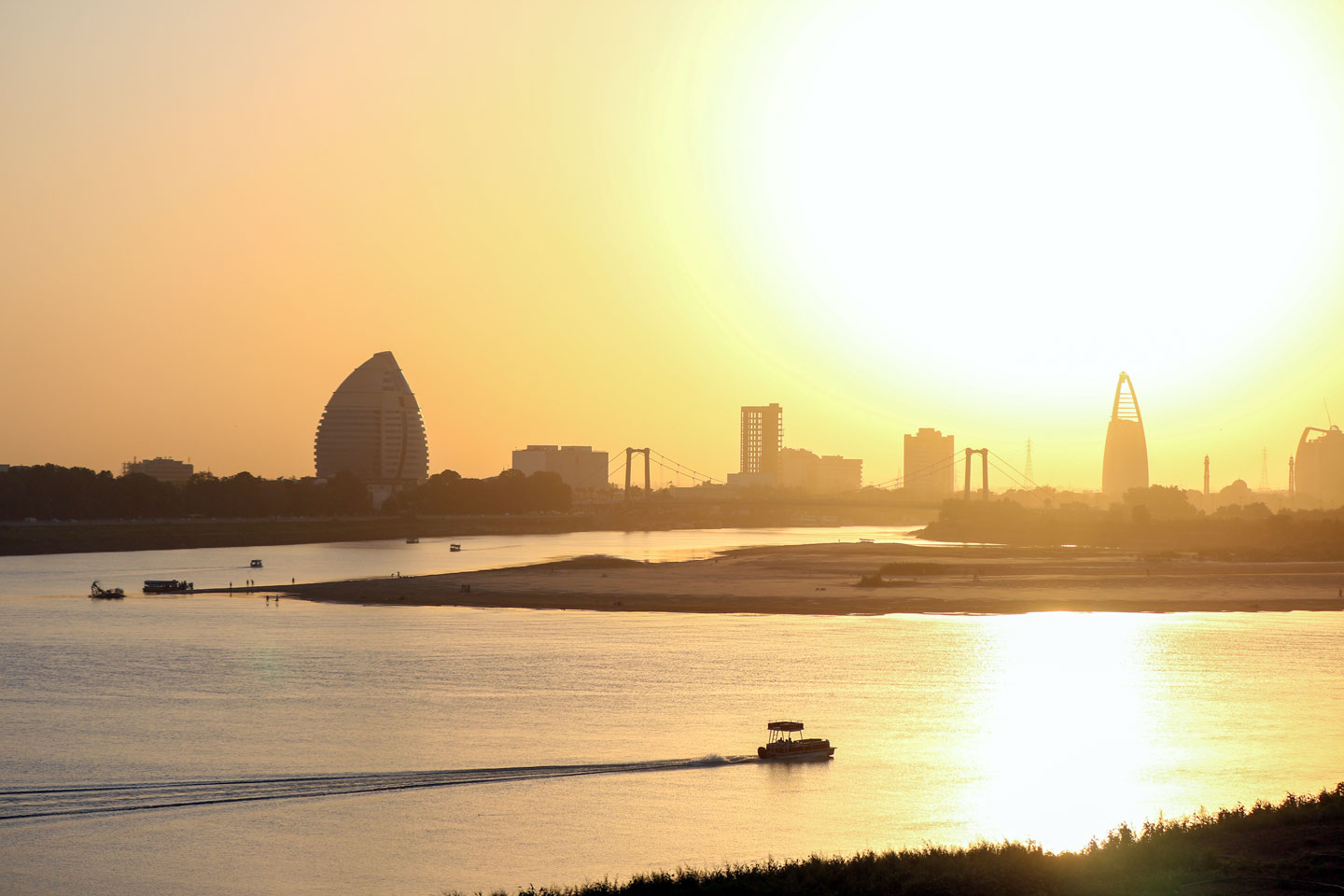 Silouette of Khartoum in the backlight. The capital of Sudan is located at the confluence of the White Nile and the Blue Nile, which together form the Nile River.
Photo: Juri Knauth
Silouette of Khartoum in the backlight. The capital of Sudan is located at the confluence of the White Nile and the Blue Nile, which together form the Nile River.
Photo: Juri Knauth
The Republic of Sudan is divided into 18 states (wilayat) and one administrative area (mintaqah). Each state is further divided into districts (mudiriyah) and counties (wilayah). The administrative area known as
Abyei Area, a piece of land on the border between Sudan and South Sudan, is administered by the Abyei Executive Council. Each state is headed by a governor, who is appointed by the president of Sudan.
Each state in Sudan has its own unique characteristics and features. Here are some notable features of a few states:
- Khartoum
Khartoum state is home to Sudan's capital Khartoum, the largest city of Sudan, Omdurman and Khartoum North (also known as Bahri). The three cities border each other and form the Khartoum metropolitan area, collectively known as the "tri-capital" area. It is the country's political, cultural, and commercial center and the most populated state.
- Red Sea
The Red Sea state is located in the Itbay region in the northeast and has a coastline along the Red Sea. The landscape of the state is characterized by the Red Sea Hills. The mountain range separates the narrow coastal plain from the Eastern Desert (Nubian Desert.) It is home to Port of Sudan, the country's main seaport. In the north of the state is the Halaib Triangle, a disputed region between Sudan and Egypt.
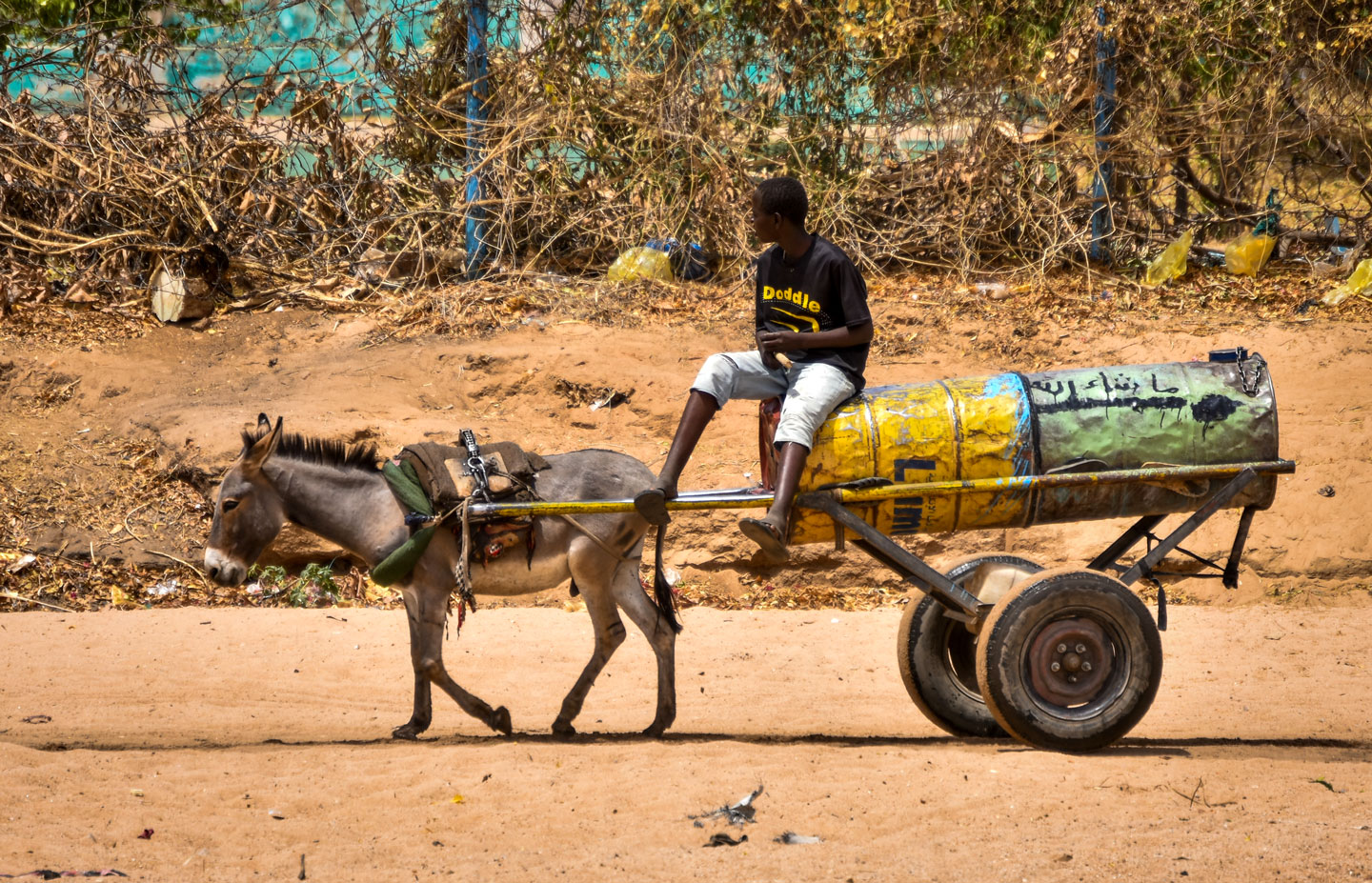 Donkeys and donkey carts are ubiquitous in Sudan.
Photo: Ramah Al-Zubair
Donkeys and donkey carts are ubiquitous in Sudan.
Photo: Ramah Al-Zubair
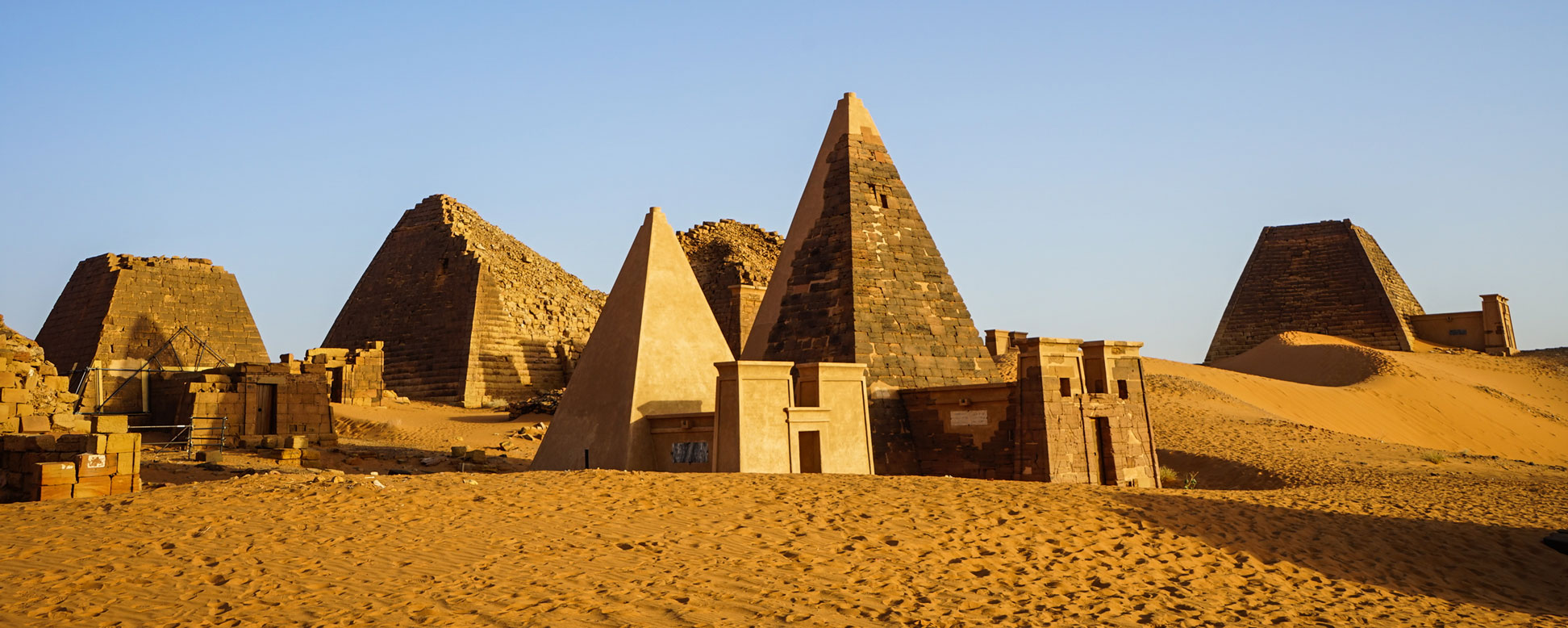
This state is named after the Nile River, which runs through it. It is known for its fertile land and agricultural production. The ancient city of Meroë, once one of the capitals of the Kingdom of Kush, is located in this state.
- North Darfur
Shamal Darfur is known for its diverse landscape, which includes desert, mountains, and savannah. It is home to Jebel Marra, a volcanic mountain massif that rises up to 3,042 meters (9,980 ft) at Deriba caldera, the highest point in the country.
- South Kordofan
This state is home to the Nuba Mountains, which are known for their unique geography and cultural diversity. The region has a rich history of resistance against colonialism and authoritarian rule. The capital of the state is Kaduqli.
- Blue Nile
The state is named after the Blue Nile, a river that originates in Ethiopia and flows through Sudan. The state is known for its agricultural products, especially cotton and sesame. Its capital is Ad-Damazin.
The map shows the location of the following cities and towns:
Abri, Abu Hamad, Abu Zabad, Abyei, Ad-Damar, Ad-Damazin, Afflanda, Al Fashir, Al Fula, Al Goled, Al Junaynah (El Geneina), Al-Qadarif, Al'Atrun, Atbara, Babanusa, Berber, Buram, Dongola, El Daein, El Obeid, En Nahud, Famaka, Gadamai, Haiya, Kaduqli, Karima, Kassala, Kerma, Khartoum, Kosti, Kutum, Laqiya Arba'in, Merowe, Muglad, New Halfa, North Khartoum, Nukhayla, Nyala, Omdurman, Port Sudan, Rabak, Salala, Sawdiri, Selima Oasis, Sennar, Shendi, Sinjah, Sinkat, Suakin, Talodi, Tokar, Tullus, Um Dukhun, Umm Badr, Wad Madani, and Wadi Halfa.
Advertisements: