About Morocco
 Flag of Morocco
Flag of Morocco
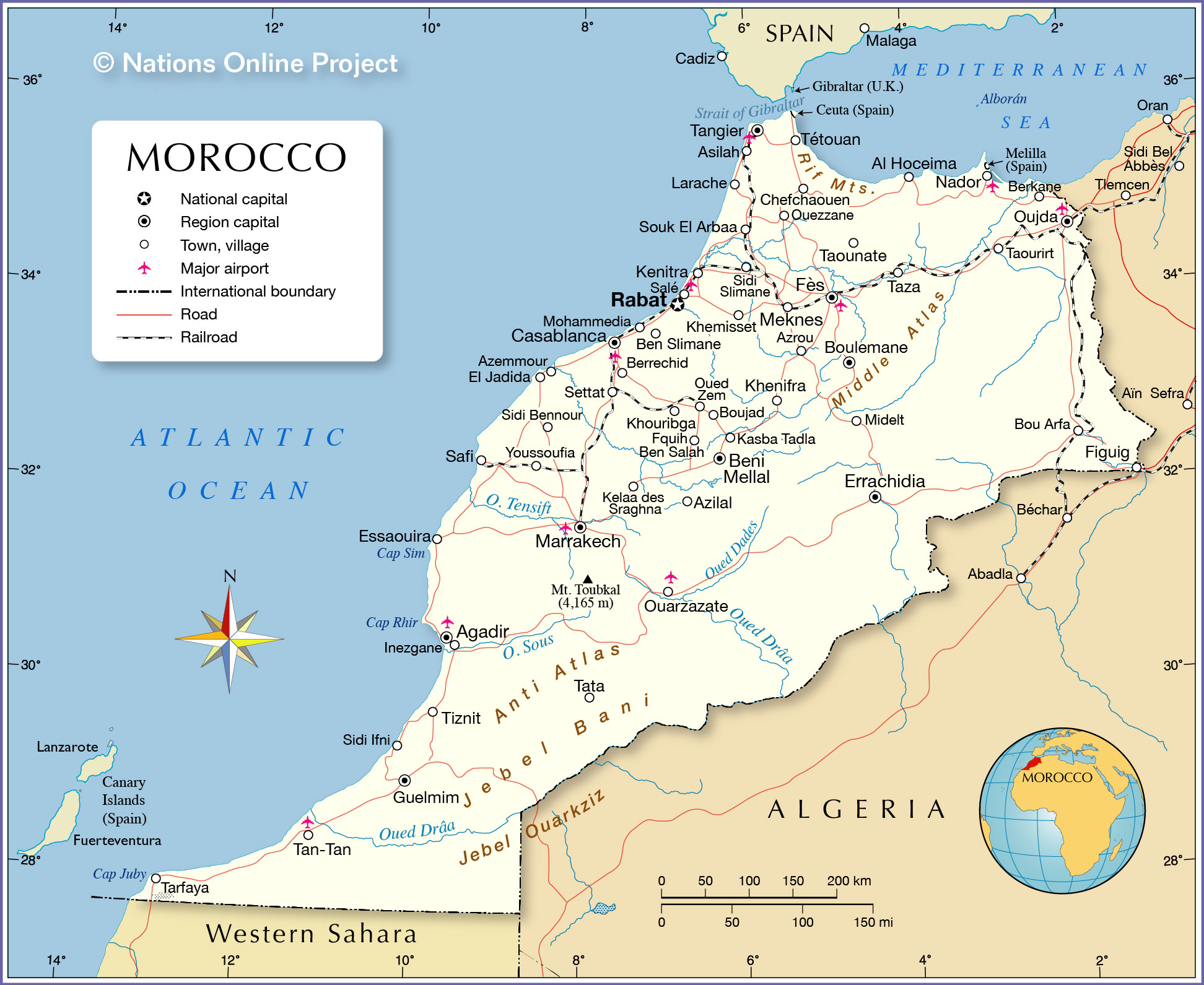
The map shows Morocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocco, a country in the western Maghreb region of North Africa. Morocco is bounded by the Atlantic Ocean in the west and the western
Mediterranean Sea in the north, it borders
Algeria in the east and
Western Sahara in the south. The non-self-governing territory is claimed by Morocco.
There are two small Spanish exclaves, Ceuta and Melilla, on the North African mainland that border Morocco.
Morocco shares maritime borders with
Portugal and
Spain.
With an
area of 446,550 km² (excluding Western Sahara), the country is somewhat smaller than
Sweden or slightly larger than
California.
Morocco has a
population of 36.3 million people; the national capital is
Rabat; the largest city is
Casablanca.
Morocco's population is a mix of Arab speaking Arab-Berbers and Berber language speaking Riffians, Chleuh (ishelhien), and Central Moroccan Imazighen (Berber). The country's official languages are Arabic and Berber (Amazigh); French is the main foreign language. The predominant religion in Morocco is Islam.
More about Morocco:
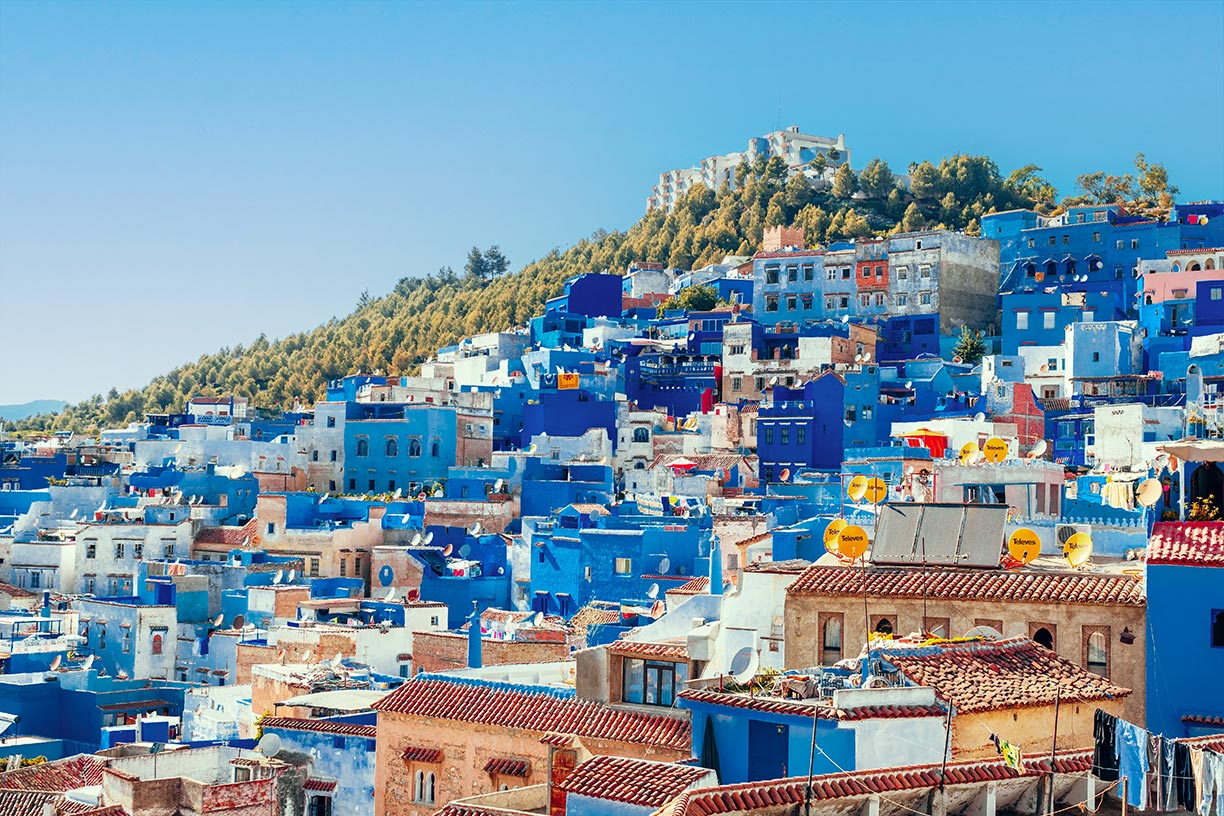 Chefchaouen is a city in the Rif Mountains of northwest Morocco; it is known worldwide for its blue-painted houses. The town is situated about 50 km inland from the Mediterranean coast.
Image: Heidi Kaden
Chefchaouen is a city in the Rif Mountains of northwest Morocco; it is known worldwide for its blue-painted houses. The town is situated about 50 km inland from the Mediterranean coast.
Image: Heidi Kaden
the coasts of the Mediterranean Sea, the Atlantic coast, the Rif mountains, the Atlas mountain ranges and the Sahara.
The westernmost of the five Maghreb countries borders the
Strait of Gibraltar and the Mediterranean Sea to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and Algeria to the east.
Along the border with Algeria, in the southeastern part of the country and in the southern region, the landscape is characterized by the fringes of the
Sahara, the largest desert in the world. The area includes the
Tafilalt Basin in the eastern Anti-Atlas and the
Draa river basin.
Morocco's coasts
Morocco's
Atlantic coast is a flat, barely indented graded shoreline with heavy sand transport and therefore poorly suited for harbors.
Nevertheless, some of the most important cities are located on the coast of the Moroccan Atlantic lowlands, such as Tangier, the capital Rabat, Casablanca and Agadir.
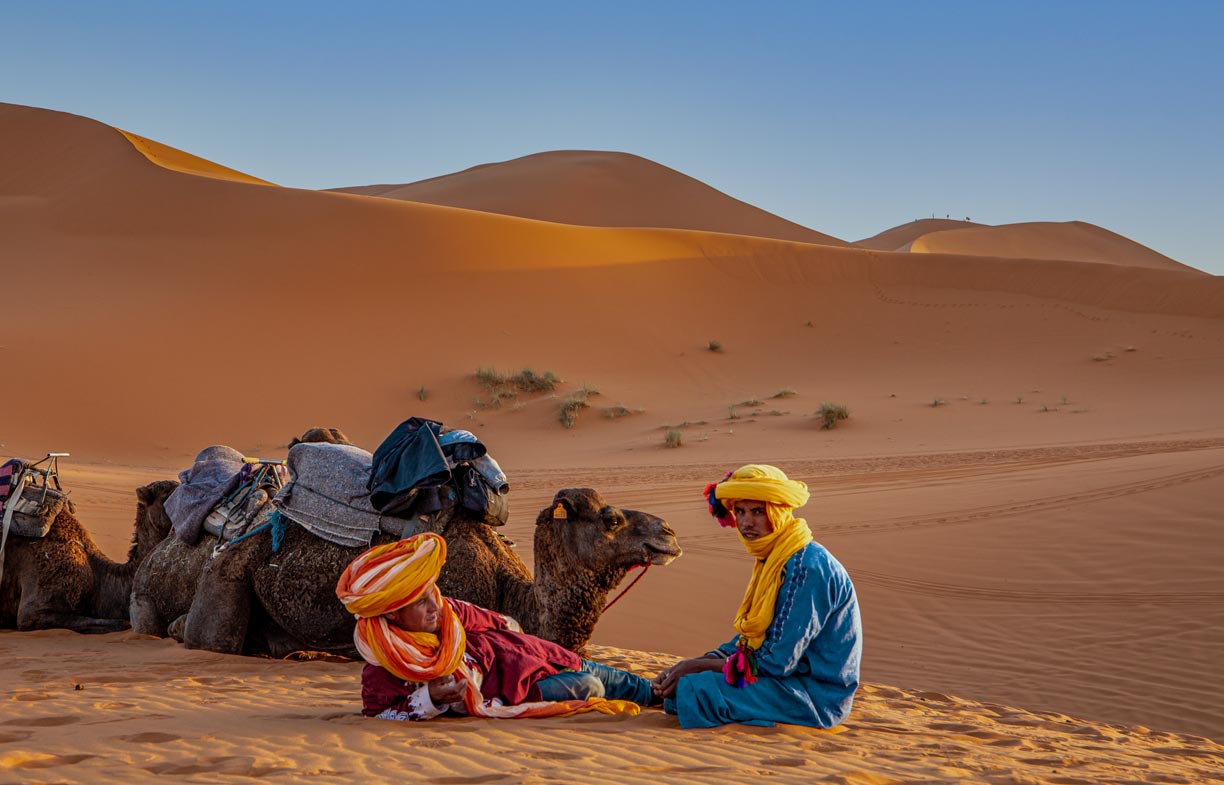 Berber people near Merzouga, a small Moroccan town in the Sahara Desert near the Algerian border. The village is known as a gateway to the Erg Chebbi, an area with large seas of dunes north of Merzouga.
Berber people near Merzouga, a small Moroccan town in the Sahara Desert near the Algerian border. The village is known as a gateway to the Erg Chebbi, an area with large seas of dunes north of Merzouga.
Photo: Tatiana Zanon
Morocco is largely mountainous. The northern part is dominated by the
Rif Mountains, a fertile geographic and cultural region inhabited by (Rif) Berbers since prehistoric times. Southeast of the Rif Mountains is the
Middle Atlas, a mountainous area where snow-capped peaks rise to over 2,000 meters.
In the center of the country is are Morocco's highest peaks. They belong to the lofty
High Atlas Mountains, part of the Atlas Mountains, a large mountain range that extends across northwestern Africa from Tunisia to the Atlantic coast in Morocco.
Within the High Atlas is the country's highest peak,
Mount Toubkal at 4,165 m. The mountain is part of the
Toubkal National Park, the first national park in the country, established in 1942.
Further southwest of the High Atlas lies the
Anti-Atlas, a mountain range that extends from
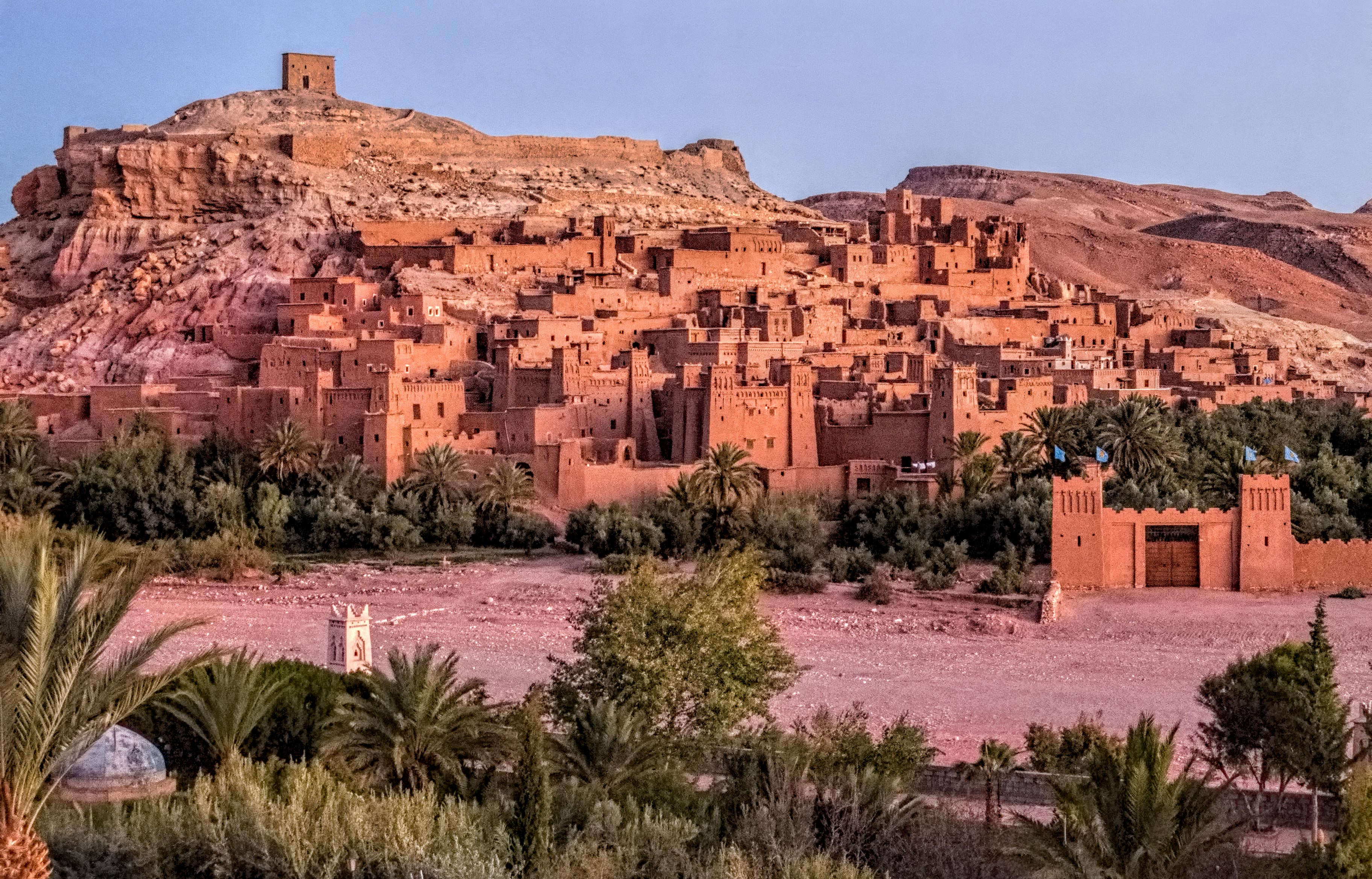
Ouarzazate, a city known as "
the door of the desert" in the northeast, towards the Atlantic Ocean in the southwest.
Rivers
Morocco's river system is the most extensive in North Africa. Important rivers are the
Moulouya River, which flows into the Mediterranean Sea near Saïdia, and the
Sebou River. The largest North African river by volume is crucial for irrigation in one of Morocco's most fertile regions, the Gharb basin. The
Draa River in the south is Morocco's longest river, at 1,100 km; the Draa valley is famous as the date basket of Morocco.
Cities and airports
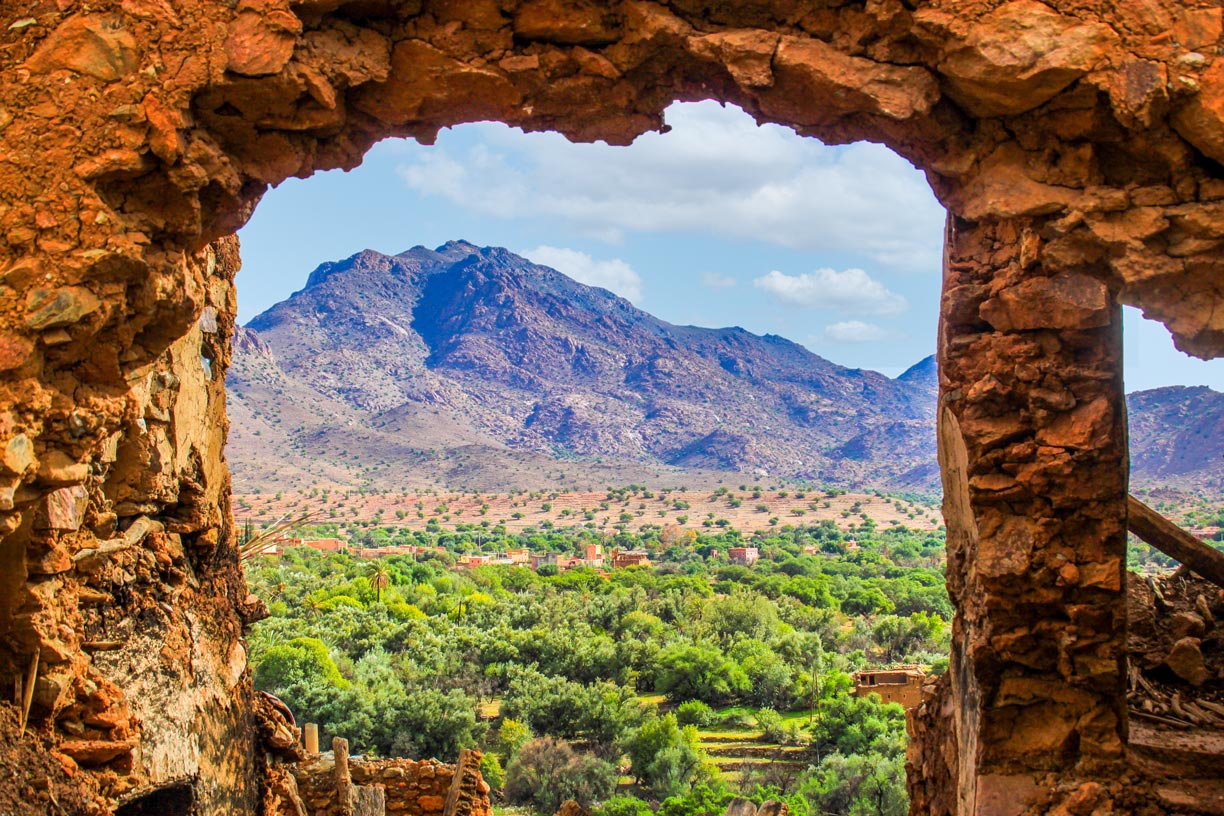 Oasis landscape in the Atlas mountains.
Oasis landscape in the Atlas mountains.
Photo: Simohnt
Major cities are the capital
Rabat,
Casablanca, Fès,
Marrakesh, Meknes, Oujda, Salé and
Tangier.
The busiest airport in Morocco is
Mohammed V International Airport (
IATA Code: CMN), located in Nouasseur, 30 km southeast of Casablanca.
Other international airports are:
Marrakesh Menara Airport (IAK), Nador International Airport (NDR) in Nador;
Rabat–Salé Airport (RBA) in Salé; and Tangier Ibn Battouta Airport (TNG) in Tangier.
Natural resources of Morocco
Morocco has sizeable deposits of phosphate (from Western Sahara; an estimated 75% of the world's known phosphate reserves), iron, lead, zinc, barite, copper, bentonite, fluorine, manganese, salt, cobalt, silver, gold and rare earth.
Natural hazards
Morocco is prone to earthquakes; northern Morocco is near the boundary between the African and Eurasian plates, where the African plate is subducted under the Eurasian plate. Other hazards Morocco faces include flooding and drought.
On Friday, 8 September 2023, a 6.8 magnitude earthquake occurred in the High Atlas Mountains in Al Haouz Province. The epicenter was located near Morocco's highest mountain,
Mt. Toubkal in the Marrakesh–Safi region. The quakes were violent and catastrophic. They brought down remote mountain villages, and in the region's capital, Marrakesh, historic landmarks were destroyed and the old medina in the center damaged. More than 2,800 people were killed and many more are still missing.
Environmental issues
The country's main problem is desertification; more than 90% of Morocco's land area is more or less deserted. The land degradation is mainly due to anthropogenic influences (caused by humans) and is accelerated by climate change and prolonged droughts. Bushfires, overgrazing, and deforestation are among the perceived causes of desertification in the country.
The map shows the location of following Moroccan cities, towns (major cities in bold):
Agadir, Al Hoceima, Asilah, Azemmour, Azilal, Azrou, Ben Slimane, Berkane, Berrechid, Béni Mellal, Bou Arfa, Boujad, Boulemane, Casablanca, Chefchaouen, El Jadida, El Kelaa des Srarhna, Errachidia, Essaouira, Fès, Figuig, Fkih Ben Salah, Guelmim, Inezgane, Kasba Tadla, Kenitra, Khemisset, Khenifra, Khouribga, Larache, Marrakech, Meknès, Midelt, Mohammedia, Nador, Ouarzazate, Oued Zem, Ouezzane, Oujda, Rabat, Safi, Salé, Settat, Sidi Bennour, Sidi Ifni, Sidi Slimane, Souk el Arba du Rharb, Tan-Tan, Tangier, Taounate, Taourirt, Tarfaya, Tata, Taza, Tétouan, Tiznit, and Youssoufia.
Advertisements: