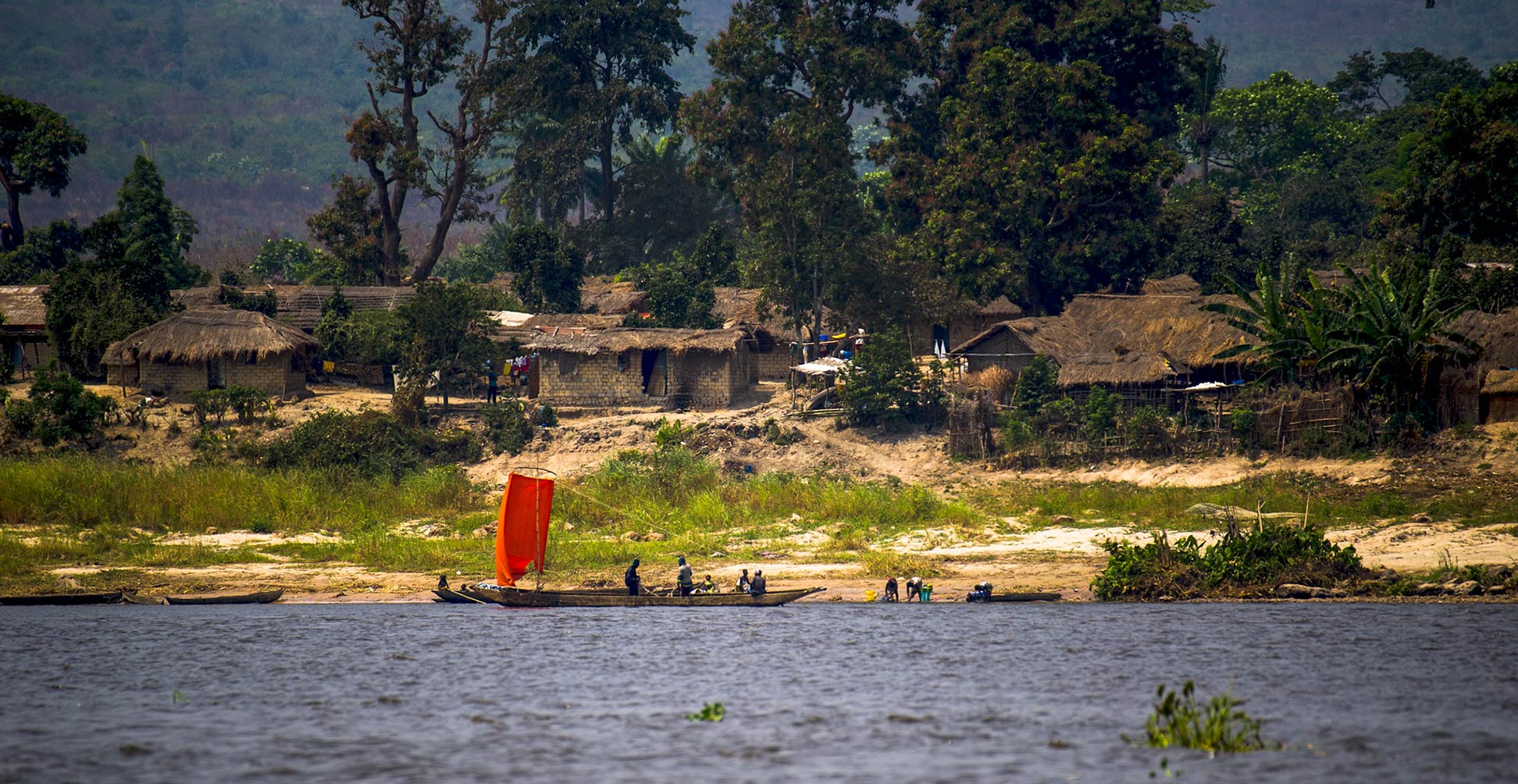
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) is one of the largest countries in Africa. The nation in the heart of the continent has a short coastline on the Atlantic Ocean. The capital is
Kinshasa; spoken languages are French (official), Kikongo, Lingala, Swahili, and others. Main religion is Christianity.
The country's political system has been crippled in recent years by the manipulation of electoral laws and procedures by political elites. Citizens are unable to exercise fundamental civil liberties freely, and corruption is endemic throughout the government. Physical security is compromised due to violence and human rights abuses by government forces, armed rebel groups, and militias active in many areas of the country.
Despite fertile land, hydropower potential, and mineral resources, the DRC struggles with many socioeconomic problems, including high child and maternal mortality rates, frequent and early fertility, malnutrition, food insecurity, lack of access to clean water and sanitation.
[8]