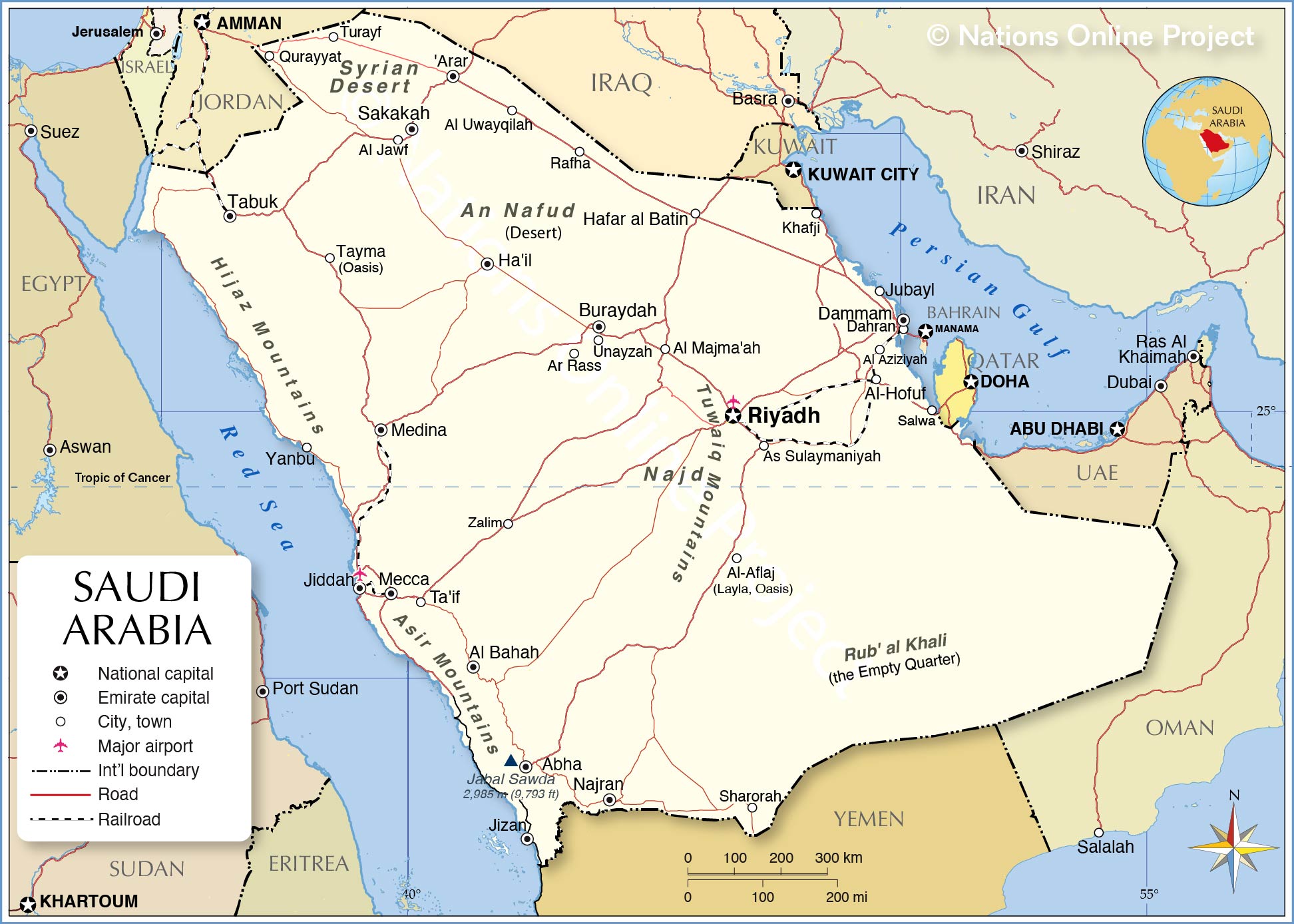
About Saudi Arabia
The map shows Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, a desert country in southwestern Asia (Middle East) that occupies most of the
Arabian Peninsula.
The kingdom is bounded by the Gulf of Aqaba and the
Red Sea in the west and the Persian Gulf in the east. Border countries are
Iraq,
Jordan,
Kuwait,
Oman,
Qatar,
United Arab Emirates, and
Yemen. Saudi Arabia shares maritime boundaries with
Egypt,
Sudan, and
Eritrea in the Red Sea, and with
Iran, and
Bahrain in the Persian Gulf.
The country is the largest Arab state with a
land area of more than two million km²; compared, the sheikdom is about four times the size of
France, or somewhat larger than one quarter the size of the contiguous United States.
Saudi Arabia has a
population of 34.8 million people (in 2020); more than 10 million people are expatriates, mainly from Asia and the Middle East.
Saudi Arabia is the homeland of Arab Bedouins and the Arabian language, the historic birthplace of Islam and the Arab-Islamic culture which originated in the towns of
Mecca and Medina at the beginning of the 7th century.
The country's capital and largest city is
Riyadh. Other major towns are Jiddah,
Ta'if (At Taif), Dammam, Buraydah, and Al Khobar, part of the Dammam metropolitan area. Spoken
language is Arabic.
More about Saudi Arabia
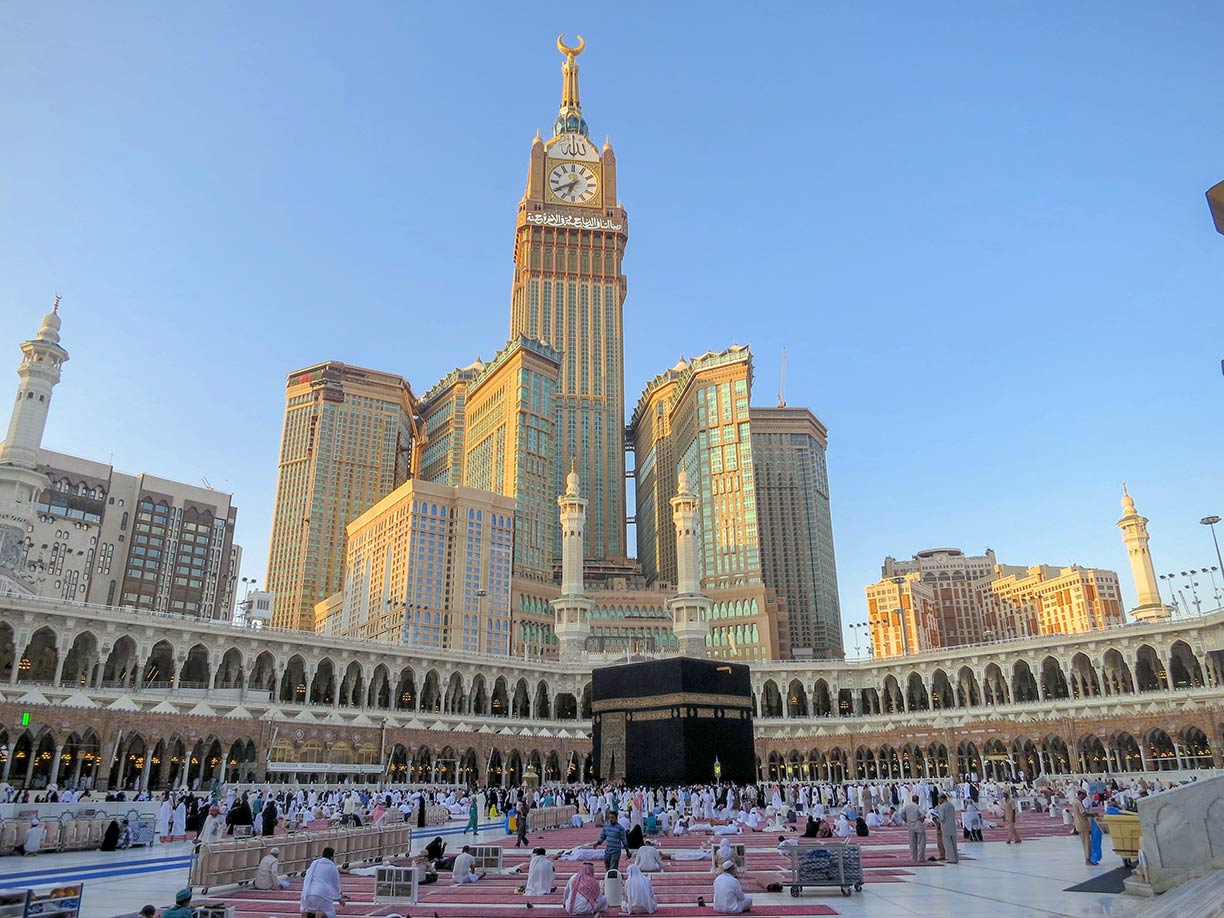 Al-Masjid Al-Ḥarām, the Great Mosque of Mecca. Located within the largest mosque in the world is the Kaaba, the holy shrine of Islam. Abraj Al Bait in background, a megatall hotel complex of seven skyscrapers.
Al-Masjid Al-Ḥarām, the Great Mosque of Mecca. Located within the largest mosque in the world is the Kaaba, the holy shrine of Islam. Abraj Al Bait in background, a megatall hotel complex of seven skyscrapers.
Photo: neo saed
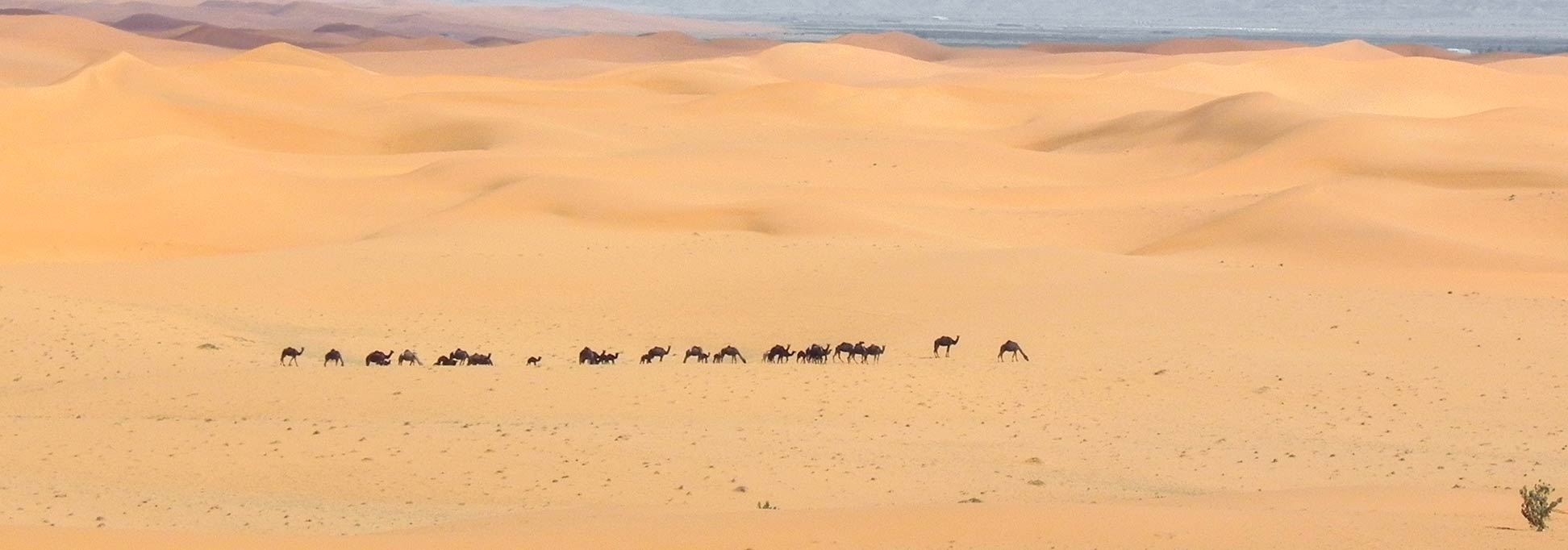
The
Arabian Desert covers large parts of the country's landscape. The vast area consists of a number of interconnected desert regions including the An Nafud in the north, and the Rub' al Khali ("the Empty Quarter") in the southern part of the country. The Rub' al Khali is one of the world's largest contiguous sand deserts.
The coastal plain in western Saudi Arabia along the Red Sea is known as the
Tihamah, the east of the plain is dominated by the escarpments of two mountain ranges, the Hejaz and the Asir mountain range, separated by a gap in the area of Mecca. The highest point of Saudi Arabia is
Jabal Sawda, the peak of about 3,000 m is located in the Abha region in the Asir mountains in the southwestern corner of the sheikdom. The one hundred kilometers wide strip of coastal plains and the western mountain ranges is known as the
Hejaz ('the Barrier'). The Hejaz separates the coastal area from the
Najd, the central region of Saudi Arabia. The Najd is bounded to the east by the historical region of Eastern Arabia, and in the north by the Syrian Desert.
There are no rivers or bodies of water in the country, only ancient river channels, now buried by the seas of sand. There are wadis, i.e. valleys or river courses, which often carry water temporarily only after heavy or prolonged rainfall. Nonrenewable fossil water from aquifers and underground rivers, water from seasonal floods, and desalinated saltwater are used for human consumption and irrigation.
Climate
Saudi Arabia has a predominantly hot and dry environment. The continental climate in the interior of the country features considerable temperature differences, especially between day and night. In summer, maximum temperatures of 50° C are possible during the day, in winter, the freezing point can be reached at night. The average annual temperature is 28° C.
Administrative regions
Saudi Arabia is divided into 13 administrative regions (or states).
The regions are (region capital in parenteses:)
Al-Bahah State (Al-Bahah)
Al Jawf State (Sakakah)
Al-Qassim State (Buraidah)
'Asir State (Abha)
Eastern Province (Dammam)
Ha'il Region (Ha'il)
Jizan State (Jizan)
Madinah State (Medina)
Makkah State (Mecca)
Najran State (Najran)
Northern Borders Region ('Ar'ar)
Riyadh State (Riyadh)
Tabuk State (Tabuk)