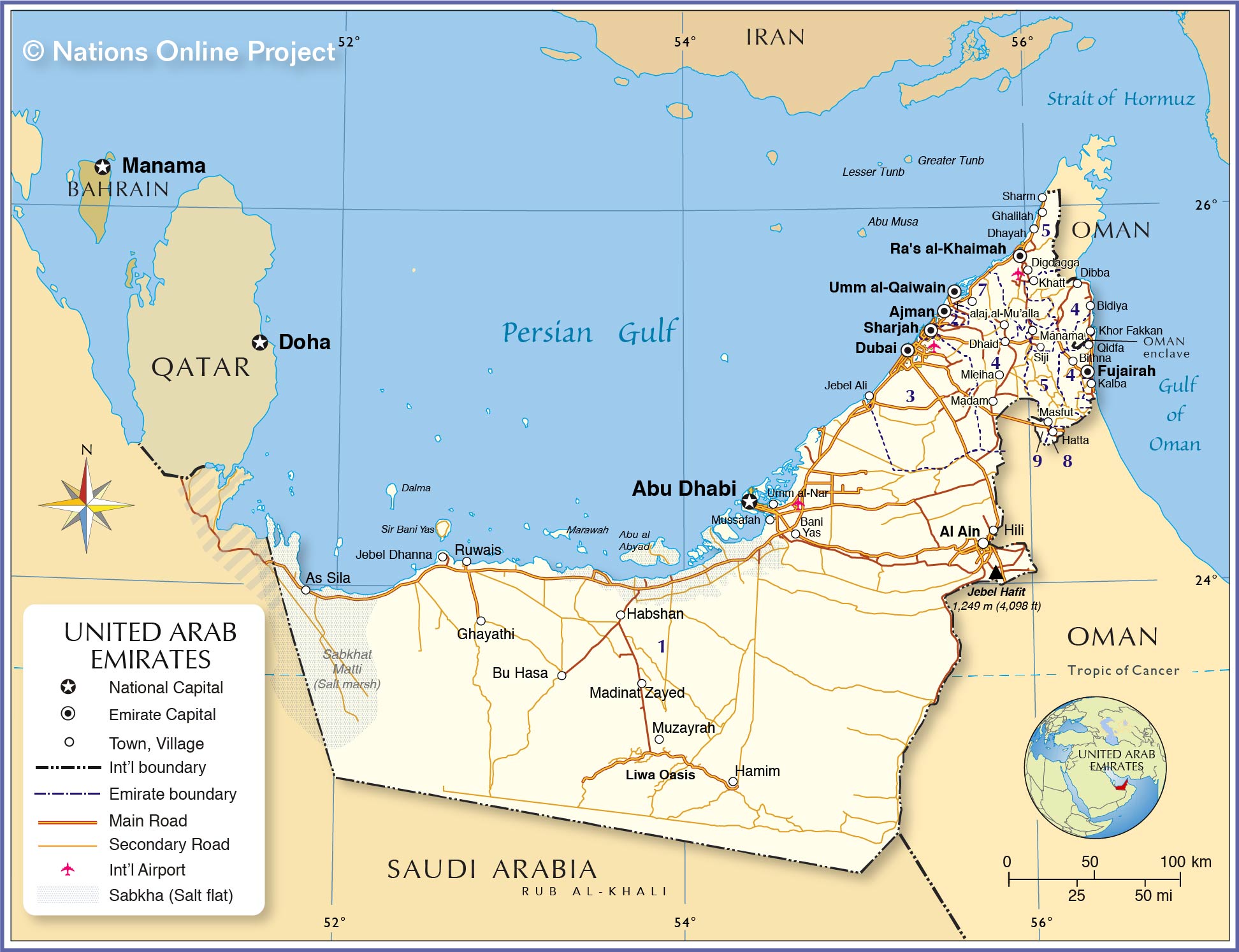
About the United Arab Emirates
The United Arab Emirates is one of the Persian Gulf States, a desert country in the southeast of the
Arabian Peninsula with a coastline at the Persian Gulf (Arab Gulf) and the Gulf of Oman. The UAE is bordering
Oman and
Saudi Arabia and has maritime borders with
Iran. There is a disputed region in the west of the Emirate of Abu Dhabi; therefore it is unclear if the UAE actually has a border with
Qatar.
[1] The coastal region of today UAE was known for a long time as the Pirate Coast. The seafaring inhabitants made a living by pirating trade vessels in the area. The loose federation of sheikdoms came under British administration in the mid 19th century, then known as the Trucial States until 1971, with the independence from the
UK.
The UAE came into existence in December 1971 when six emirates formed a federation: Abu Dhabi, Dubai, Sharjah, Ajman, Umm Al-Quwain, and Fujairah; Ras Al Khaimah joined the alliance in 1972.
With an
area of 83,600 km², the United Arab Emirates is about the size of
Austria, or slightly smaller than the US State of
Maine. The country consists mostly of barren landscape with gravel plains and desert dunes, interspersed with some oases, best known is Liwa Oasis, north of the Rub' al Khali, the Empty Quarter, the largest sand desert in the world. Along the coast stretches a strip of marshes (sabkha;) low-lying saline flats, lagoons, intertidal mudflats, and mangrove swamps. There is a mountainous region in the northeast; Jabal Yibir (1,527 m) the countries highest point is situated there.
The United Arab Emirates has a
population of 9.37 million people (in 2018), with the male population being twice as large as the female population. The capital city of the UAE is
Abu Dhabi; the largest city is
Dubai. Spoken
languages are an Emirates variant of Arabic, English is in use.