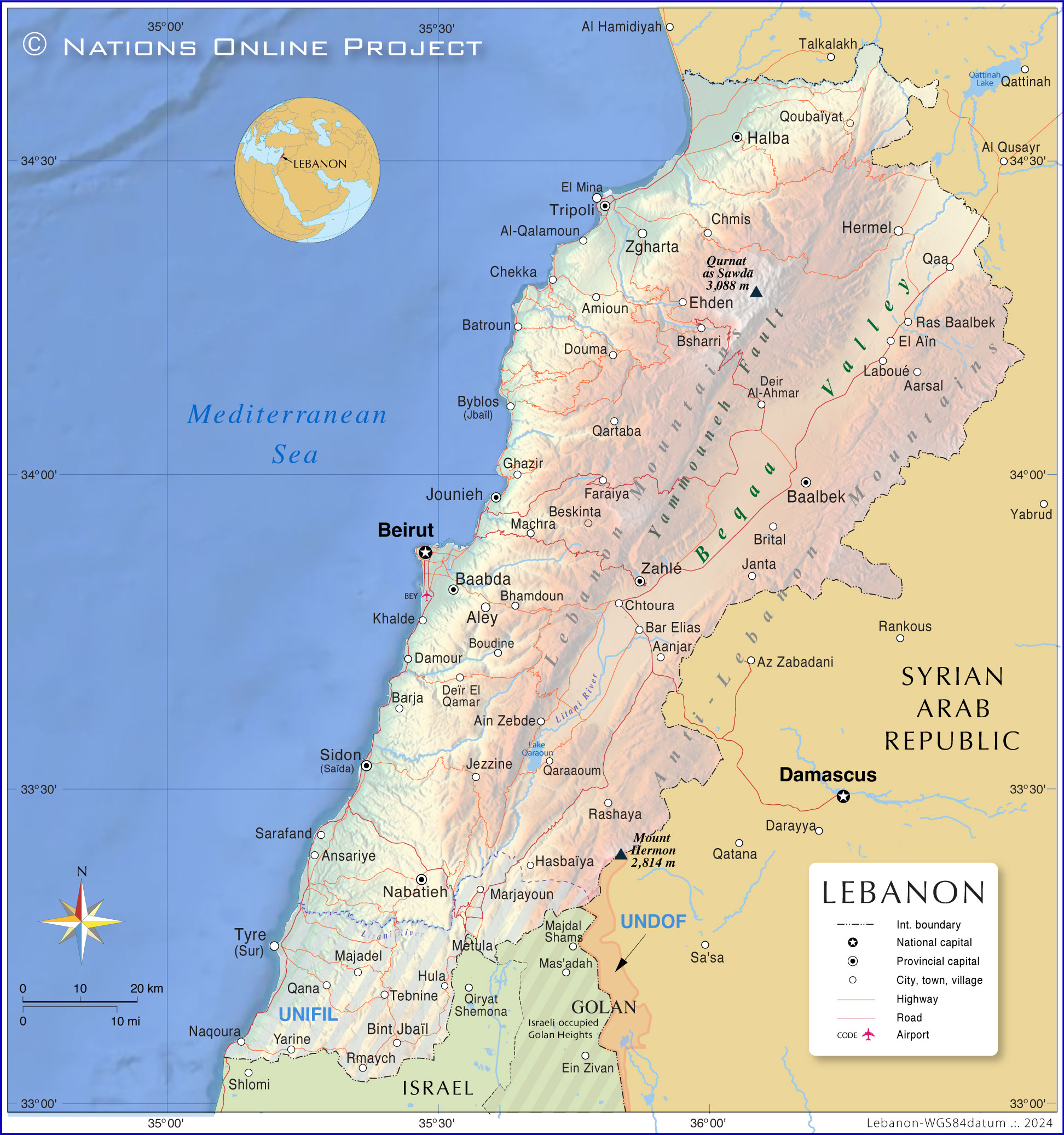
About Lebanon
The map shows Lebanon, officially the Lebanese Republic, a mountainous country in the Levant with a coastline on the eastern
Mediterranean Sea. Lebanon borders
Israel to the south and
Syria to the north and east. Most of the border between Lebanon and Syria runs through the mountainous region of the Anti-Lebanon Mountain Range. The country also shares maritime borders with
Cyprus.
The smallest nation on the Asian mainland covers an
area of 10,400 km²; compared, it is about one-third the size of
Belgium or about one-third the size of the US state of
Maryland.
Lebanon has a
population of around 5.35 million (in 2023), not including around 1.5 million refugees from Syria and Palestine.
[1] [IRF]
The majority of the Lebanese people live on or near the Mediterranean coast. The country's national capital and largest city is
Beirut. The spoken
language is Lebanese Arabic, French is also widely spoken and English is increasingly used in business and education.
Lebanon has the most religiously diverse society in the Middle East; the main religions are Islam (70%), followed by Christianity (30%), including 5% Lebanese Druze, an Abrahamic, monotheistic religion.
[IRF]
More about Lebanon
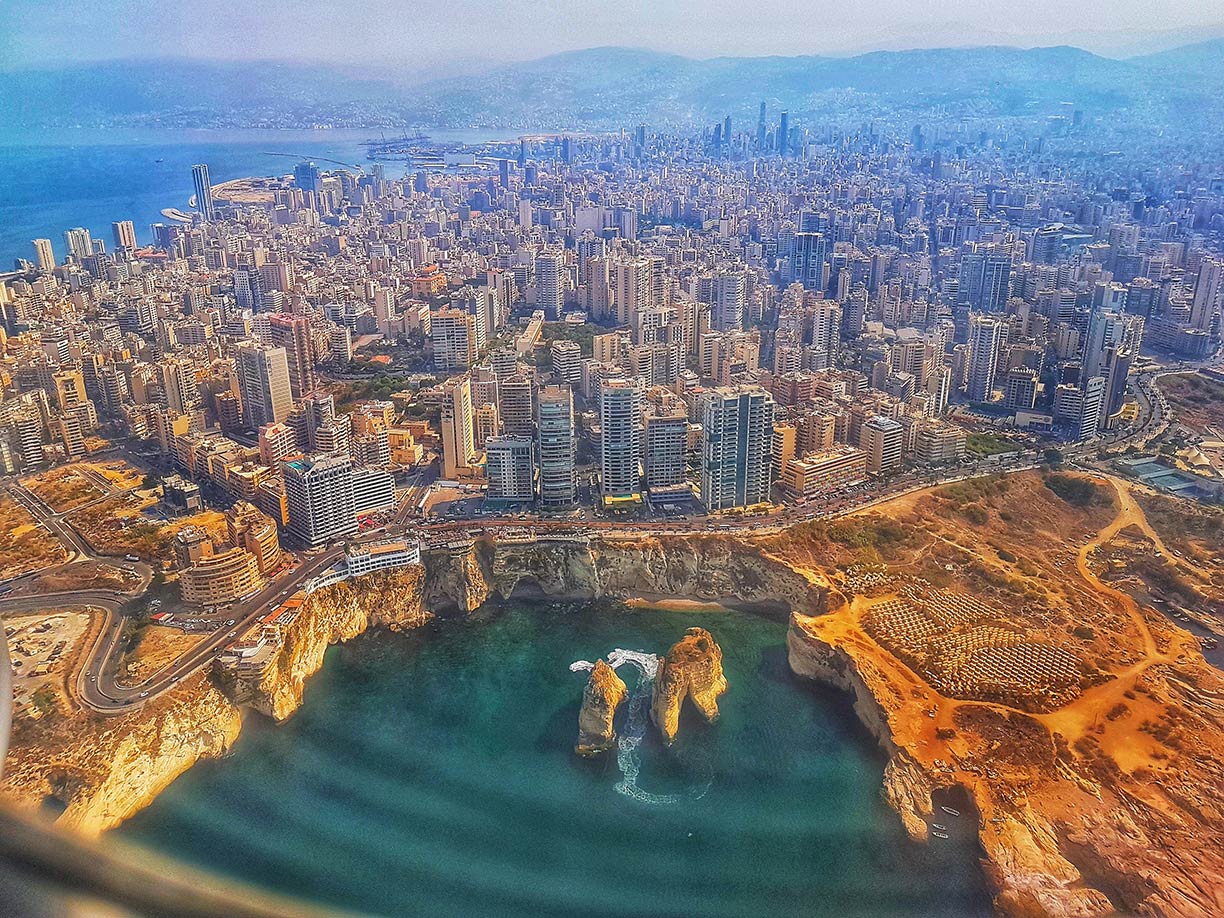 Aerial photo of Beirut at the coast of the Mediterranean Sea, capital of Lebanon.
Aerial photo of Beirut at the coast of the Mediterranean Sea, capital of Lebanon.
Photo: Alain Abou-Atmeh
Lebanon has a history that dates back thousands of years, with a rich cultural heritage. It was home to the Phoenicians, a maritime civilization that flourished for over a thousand years (c. 1550–539 BCE). In more modern times, Lebanon was part of the Ottoman Empire until the Turkish empire's dissolution following World War I, after which it came under the French mandate. Lebanon gained independence in 1943.
Lebanon's main geographical features
Lebanon has a narrow coastal strip along the Mediterranean Sea. The coast is home to most of the larger cities and towns of the country.
Agriculture in the region produces fruits and vegetables.
Mount Lebanon (Lebanon Mountains) is a mountain range that dominates the entire country; it extends parallel to the Mediterranean coast for about 195 km (120 mi). Located within the range is
Qurnat As Sawda, the Levant's highest mountain, at an elevation of 3,093 m (10,148 ft).
The
Anti-Lebanon Mountains, the "Eastern Mountains of Lebanon," are a mountain range in the east of the country. The border between Lebanon and Syria runs through it.
The
Beqaa Valley (Al-Biqā) is a high plateau at an average elevation of 1,000 m; it is situated between the Mount Lebanon range to the northwest and the Anti-Lebanon Mountains to the northeast. The valley is the northeasternmost extension of Africa's Great Rift Valley; it is a major farming region containing nearly half of Lebanon's arable land.
Primary Level Administrative Divisions of Lebanon
Lebanon is divided into eight governorates (muhafazah, Arabic: محافظات ). These governorates are from the north to the south (capitals in brackets):
Akkar (Halba); North Governorate (ash Shamal; capital is Tripoli); Baalbek-Hermel (Baalbek); Mount Lebanon (Baabda); Beirut Governorate (Beirut); Beqaa Governorate (Zahle); Nabatieh Governorate (Nabatiye) and the South Governorate (Sidon).
UNIFIL
The United Nations Interim Force in Lebanon is a multinational peacekeeping mission in southern Lebanon, in the region between the Litani River and the Lebanese-Israeli border. UNIFIL was established in 1978 following the Israeli invasion of Lebanon. Its main purpose is to monitor the cessation of hostilities and support the Lebanese Armed Forces (LAF) in restoring its authority in the region. Despite criticism of its effectiveness, UNIFIL remains a key element in maintaining peace and security in southern Lebanon and on the Lebanese-Israeli border.
Lebanese Cities
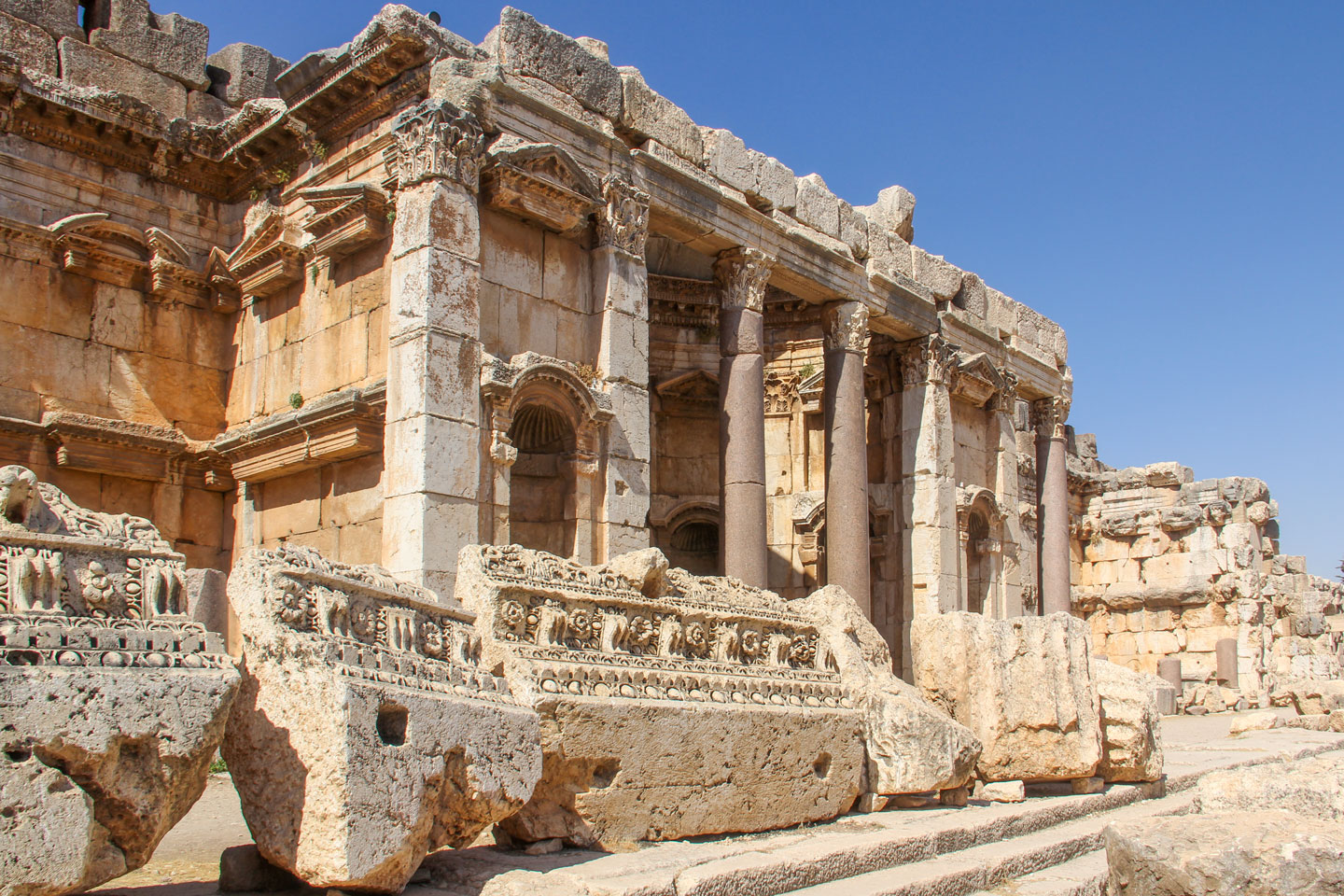 Roman ruins in Baalbek, Lebanon.
Roman ruins in Baalbek, Lebanon.
Photo: Elgaard
Almost all of Lebanon's major cities are located on the Mediterranean coast.
The country's largest city is
Beirut; the nation's capital has an estimated population of about 2 million people and is situated on a peninsula of the Mediterranean coast.
Tripoli is a seaport in northern Lebanon (not to be confused with Tripoli, the capital of Libya).
Zahlé (Zaḥlah), a city of around 150,000 inhabitants, is located in the area between the eastern foothills of the Sannine Mountains (Lebanon Mountains) on the edge of the Beqaa Plateau at an altitude of 960 meters above sea level.
Sidon was an important center of trade for the Phoenicians and later for the Persian Achaemenid Empire. The Bible describes Sidon in several passages. The city was conquered by the crusader ruler Baldwin I in 1110. Today it is the capital of Libanon's South Governorate.
Aley (Aalay; pop. 35,000) is a major Druze city known as the "Capital of the Mountains" located on Mount Lebanon, about 20 km southeast of Beirut.
Tyre (Sur), the city
is situated on a peninsula; it was an important trade center for centuries and for some time the capital of the Crusader state of the Kingdom of Jerusalem.
Tyre has been a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 1984.
Baalbek (Baʿlabakk) at the foothills of the Anti-Lebanon Mountains in the Beqaa Valley was named for Baal, the Phoenician deity; the Greeks called it Heliopolis. The former Phoenician city is the site of a number of outstanding Roman ruins.
Baalbek has been a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 1984.
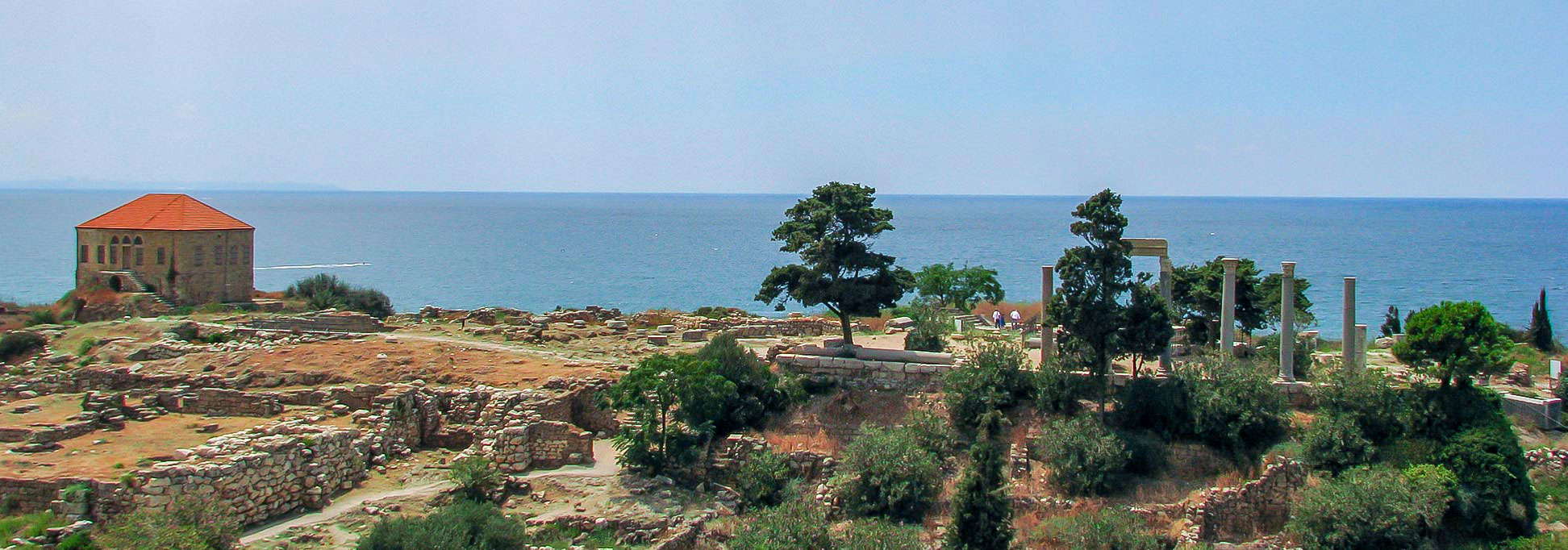
Byblos (Jbail) is a small city on the coast of the Mediterranean Sea; it was a port and trade center of the Phoenician civilization. The town has been continuously inhabited since 5000 BC.
Byblos is now a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Transportation
Beirut–Rafic Hariri International Airport, also known as Beirut International Airport (
IATA-code:
BEY), is the only airport in the country with scheduled services for commercial airlines. Beirut International is the hub for Lebanon's national carrier,
Middle East Airlines (MEA). There are no domestic flights within Lebanon due to the country's small size.
Port of Beirut
The
Port of Beirut (Arabic: مرفأ بيروت) is the most important in Lebanon and one of the largest and busiest ports on the eastern Mediterranean coast.
On 4 August 2020, the port became world-famous because of the violent explosion of a large amount of ammonium nitrate. More than 200 people were killed in the explosion, 7,000 were injured and property damage amounted to 15 billion US dollars.
Road Transportation
Lebanon has a well-developed road network, which is the primary mode of transportation within the country. Public transport is less developed and organized than in some other countries. In most areas, there are no official public bus networks but privately operated minibuses and vans.
Railways
Lebanon had a railway system that connected major cities and towns. However, the
Lebanese Civil War (1975-1990) severely damaged the rail infrastructure, leaving it largely out of service.
The map shows the location of the following Lebanese cities and towns:
Aanjar, Aarsal, Ain Zebde, Al-Qalamoun, Aley, Amioun, Ansariye, Baabda, Baalbek, Bar Elias, Barja, Batroun, Beirut, Beskinta, Bhamdoun, Bint Jbaïl, Boudine, Brital, Bsharri, Byblos (Jbaïl), Chekka, Chmis, Chtoura, Damour, Deir Al-Ahmar, Deïr El Qamar, Douma, Ehden, El Aïn, El Mina, Faraiya, Ghazir, Halba, Hasbaïya, Hermel, Hula, Janta, Jezzine, Jounieh, Khalde, Laboué, Machra, Majadel, Marjayoun, Metula, Nabatieh, Naqoura, Qaa, Qana, Qaraaoum, Qartaba, Qoubaïyat, Ras Baalbek, Rashaya, Rmaych, Sarafand, Sidon (Saïda), Tebnine, Tripoli, Tyre (Sur), Yarine, Zahlé and Zgharta.
Advertisements: