More about Greece
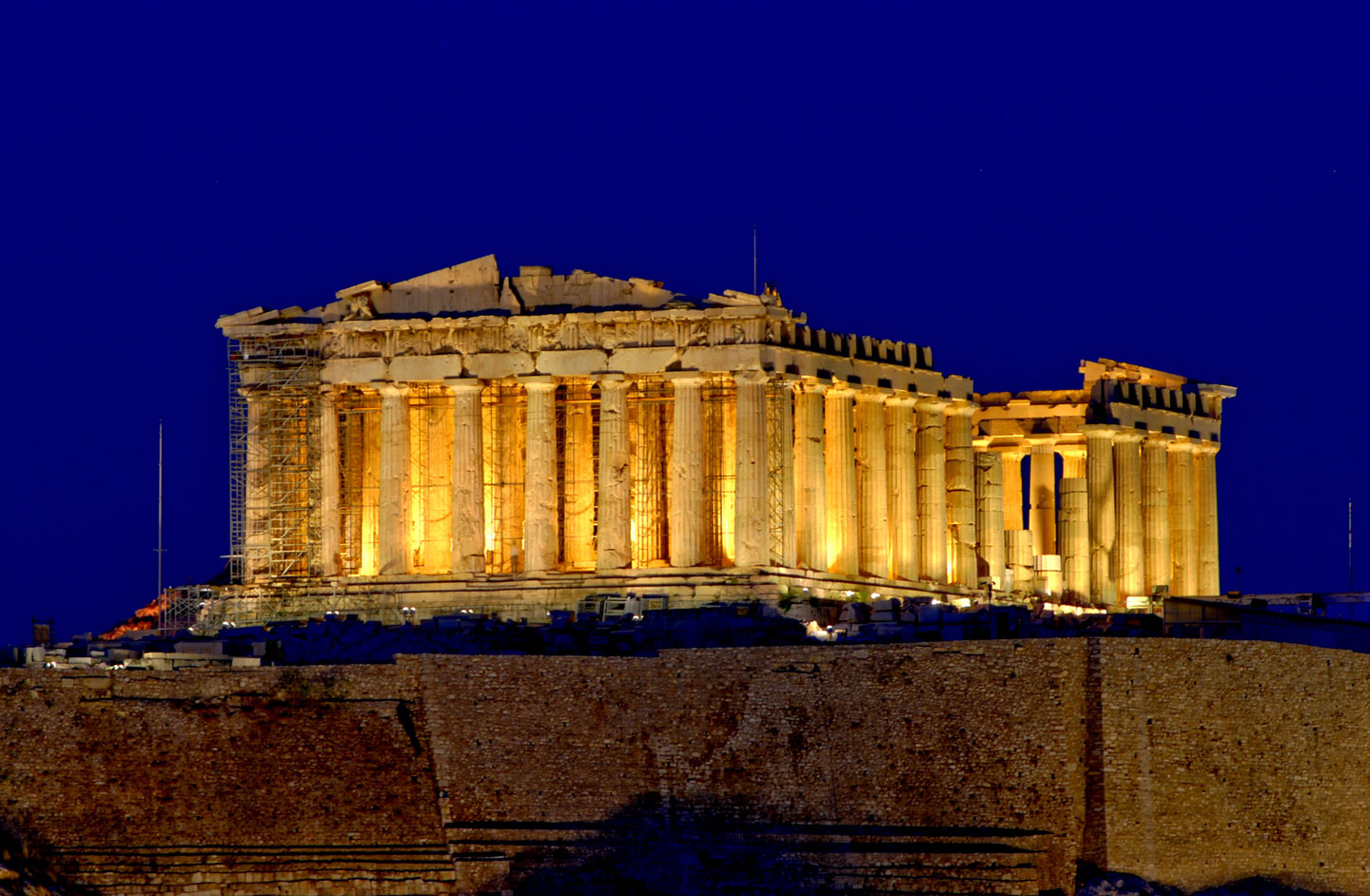 Built between 447 and 438 BC, the Parthenon on the Acropolis is one of the most important monuments of the ancient Greek civilization and possibly the most photographed building in Greece. The temple was dedicated to Athena, one of the twelve chief Olympian deities. The almost 2,500-year-old sanctuary and other monuments of the Acropolis of Athens are a UNESCO World Heritage Site and a major tourist attraction.
Photo: Dafalias
Built between 447 and 438 BC, the Parthenon on the Acropolis is one of the most important monuments of the ancient Greek civilization and possibly the most photographed building in Greece. The temple was dedicated to Athena, one of the twelve chief Olympian deities. The almost 2,500-year-old sanctuary and other monuments of the Acropolis of Athens are a UNESCO World Heritage Site and a major tourist attraction.
Photo: Dafalias
came into existence following the War of Independence against the Ottoman Empire (Türkiye) in the early 19th century, leading to its recognition as an independent nation in 1830.
The country is known for being the cradle of
Western civilization and the idea of
democracy. The word democracy comes from the Greek words "demos" (δῆμος) for people and "kratos" (κράτος) for power or rule or strength.
Ancient Greek philosophy laid the foundations for many areas of Western thought, from ethics and metaphysics to epistemology and politics.
Much of the early politics, artistic thought (architecture, sculpture), scientific thought, theater, literature, and philosophy of Western civilization came from the
Classical Greece period of Greek history (between the 5th and 4th centuries BCE), which had a strong influence on the
Roman Empire.
Among the great Greek thinkers, the most famous are probably
Socrates,
Plato,
Pythagoras and
Aristotle.
In the Hellenistic Period (3rd century BCE - 3rd century CE), new philosophical schools emerged, such as Stoicism, Epicureanism,
Skepticism and Cynicism.
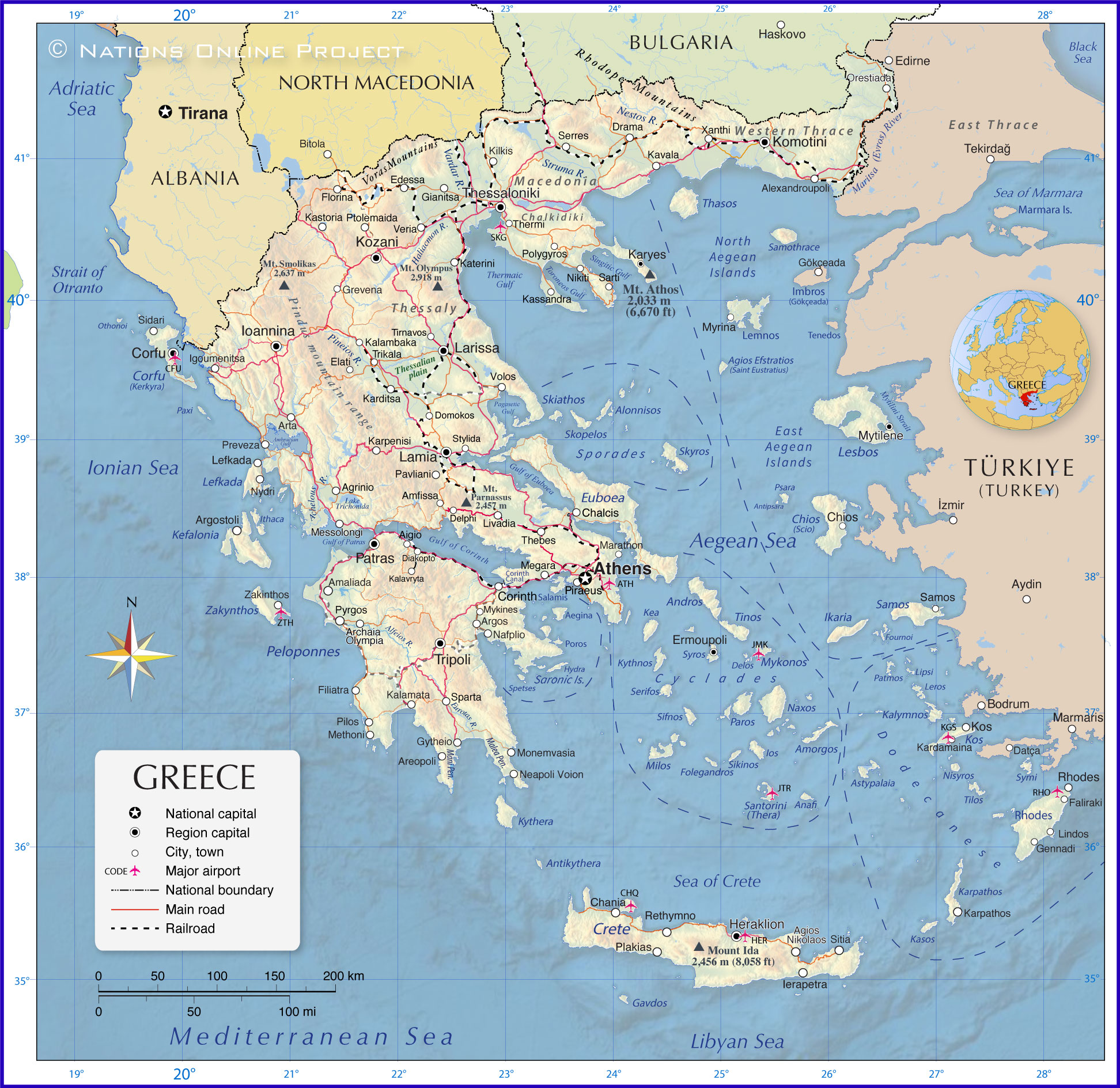
Greece Geography
Greece is situated on the
Balkan Peninsula, which juts into the Mediterranean Sea. The diverse landscape of Greece is characterized by a rugged terrain of mountains, valleys and plains on the mainland and thousands of small and big islands in the Mediterranean.
Mountainous Terrain
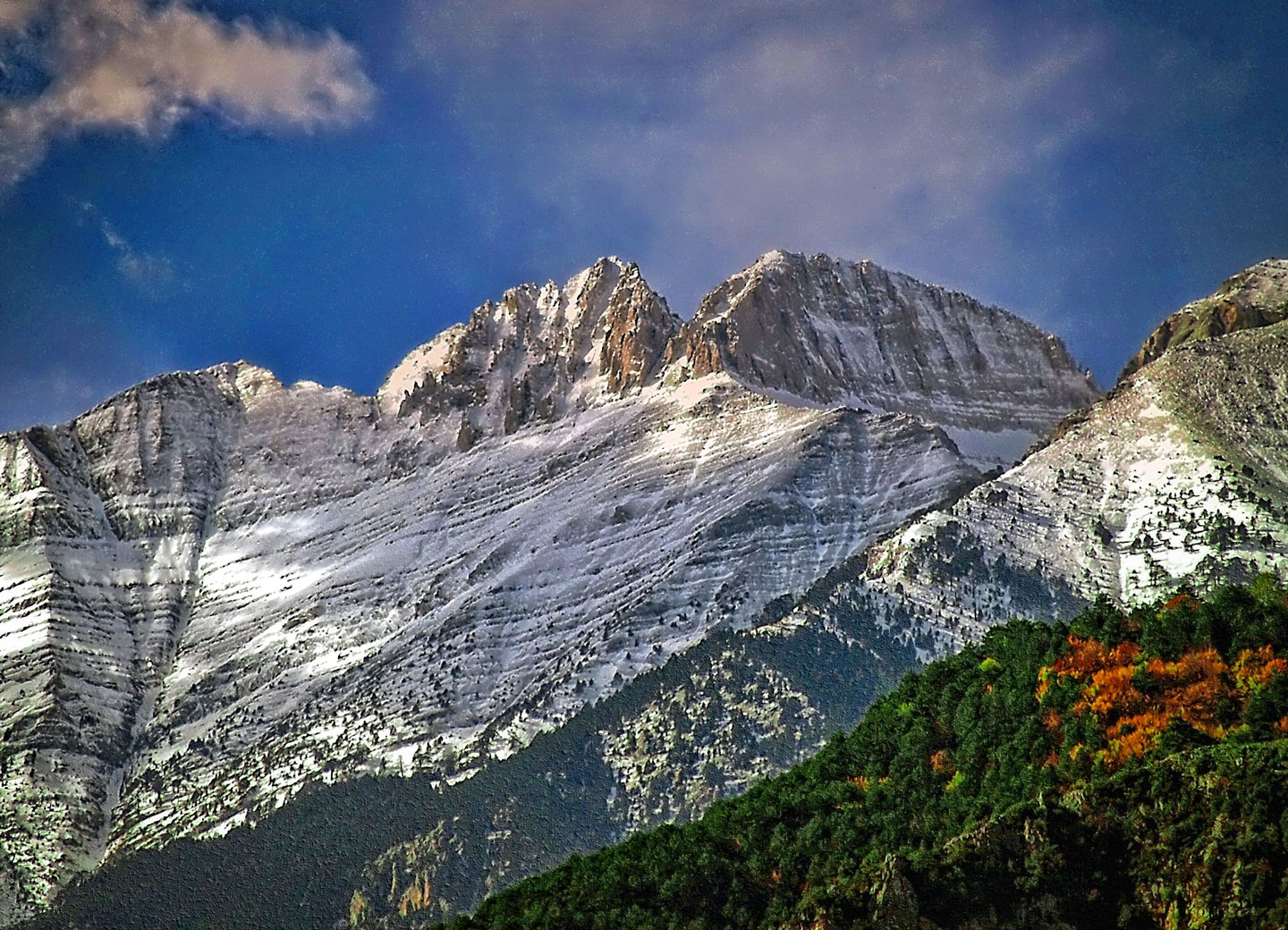 Mount Olympus with Mytikas and Skolio, the two highest peaks in the Olympus mountain range. Mount Olympus is Greece's highest mountain and, in ancient times, the realm of Zeus, who reigned as king over a motley crew of ancient Greek gods.
Photo: Teogera
Mount Olympus with Mytikas and Skolio, the two highest peaks in the Olympus mountain range. Mount Olympus is Greece's highest mountain and, in ancient times, the realm of Zeus, who reigned as king over a motley crew of ancient Greek gods.
Photo: Teogera
The
Pindus mountain range runs north-south along the mainland. Other mountain ranges are the
Rhodope Mountains shared by Greece and Bulgaria, the
Voras Mountains on the Greek-North Macedonian border, the Naxos Mountain Range on Naxos, the Santorini Mountains on Santorini island, and the
Olympus massif on the border between
Thessaly and
Macedonia, about 50 km (30 mi) north of
Larissa, the largest city of the Thessaly region.
Mountains played a crucial role in shaping Greek civilization, often isolating communities from one another and thereby fostering the development of individual city-states. Famous Greek mountains are
Mount Olympus, which is, with an elevation of 2,918 m (9,573 ft), the highest mountain in Greece and the residence of the
Greek gods, and
Mount Athos, a mountain on the Athos peninsula and an important center of Eastern Orthodox monasticism. The mountain and most of the Athos peninsula are governed as an autonomous region by an Eastern Orthodox community of monks, the "Monastic community of Mount Athos."
Valleys and Plains
Between the mountainous areas lie fertile valleys and plains, where agriculture thrives. The
Thessalian Plain is one of the country's largest and most significant agricultural areas.
Seas and Coastlines
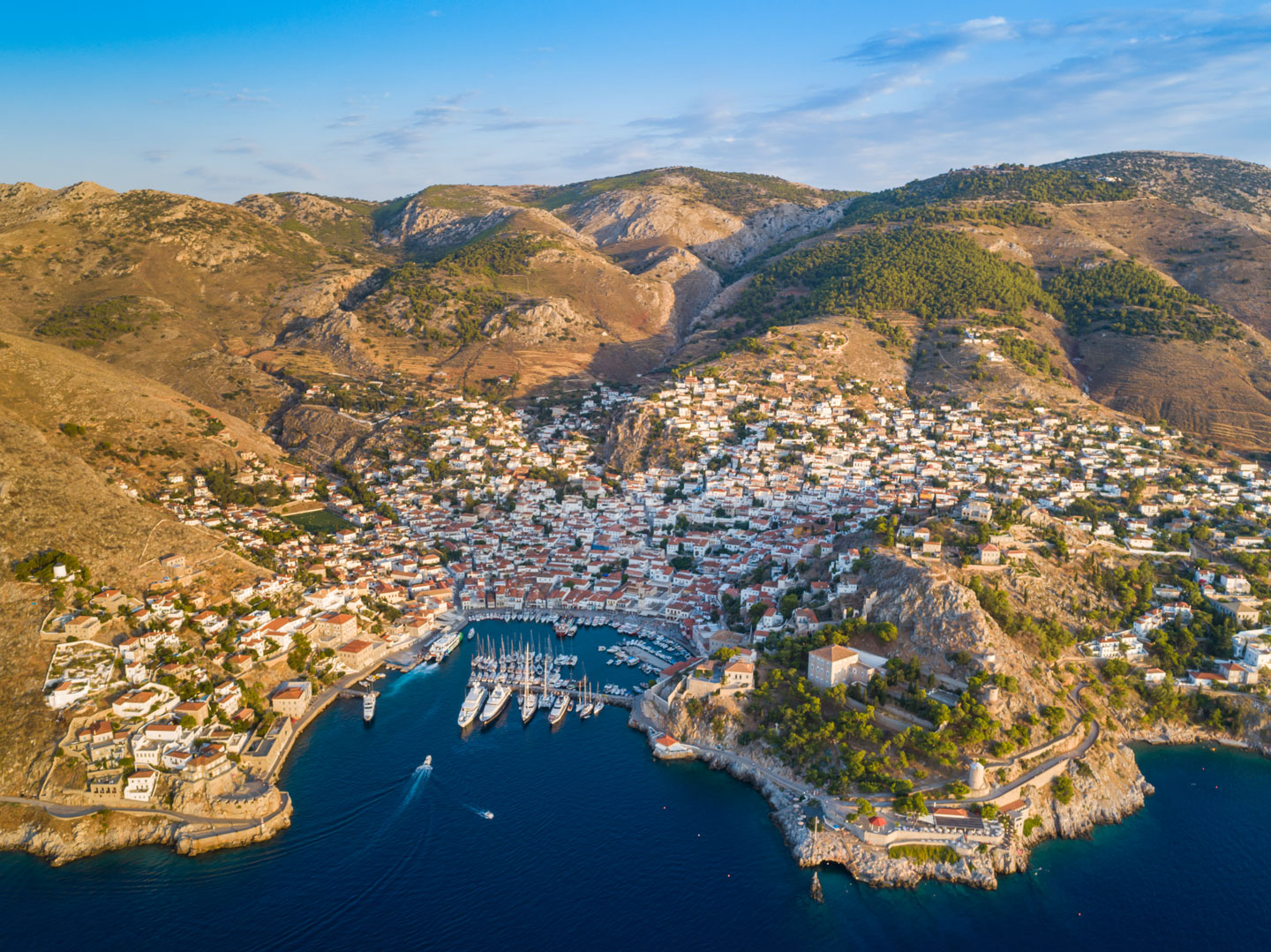 The port of Hydra on the island of the same name. The name Hydra comes from the ancient Greek word ὕδρα (hydra), their word for "water." Hydra is also the name of a serpentine water monster in Greek and Roman mythology.
Photo: dronepicr
The port of Hydra on the island of the same name. The name Hydra comes from the ancient Greek word ὕδρα (hydra), their word for "water." Hydra is also the name of a serpentine water monster in Greek and Roman mythology.
Photo: dronepicr
Greece is surrounded by seas on three sides: the
Aegean Sea to the east, the
Ionian Sea to the west, and the
Mediterranean Sea to the south. These waters were vital for Greek trade, transportation, communication, and maritime skills.
Islands
Greece has about 6,000 islands, most of which are located in the Aegean Sea
[VG]. The
Cyclades, the
Dodecanese, the
Ionian and the
Saronic islands are the major archipelagos.
Greece's largest islands are Crete, Evia (Euboea), Lesbos, Rhodes and Chios.
The Greek islands played a significant role in the development of Greek seafaring skills, trade and culture. The islands acted as hubs for trade routes, linking mainland Greece with Asia Minor (Anatolia, Turkey), the
Black Sea region,
Egypt, and beyond. Seafaring skills and trade facilitated the exchange of goods and ideas, which influenced Greek and Roman culture.
See a list of the
Greek islands below.
Rivers & Lakes
Unlike some ancient civilizations that developed around major river systems, Greece doesn't have very large rivers. However, smaller rivers like the Alpheus, Achelous, and the Evros were essential for irrigation and other uses.
The largest natural lake in Greece is
Lake Trichonida.
Climate
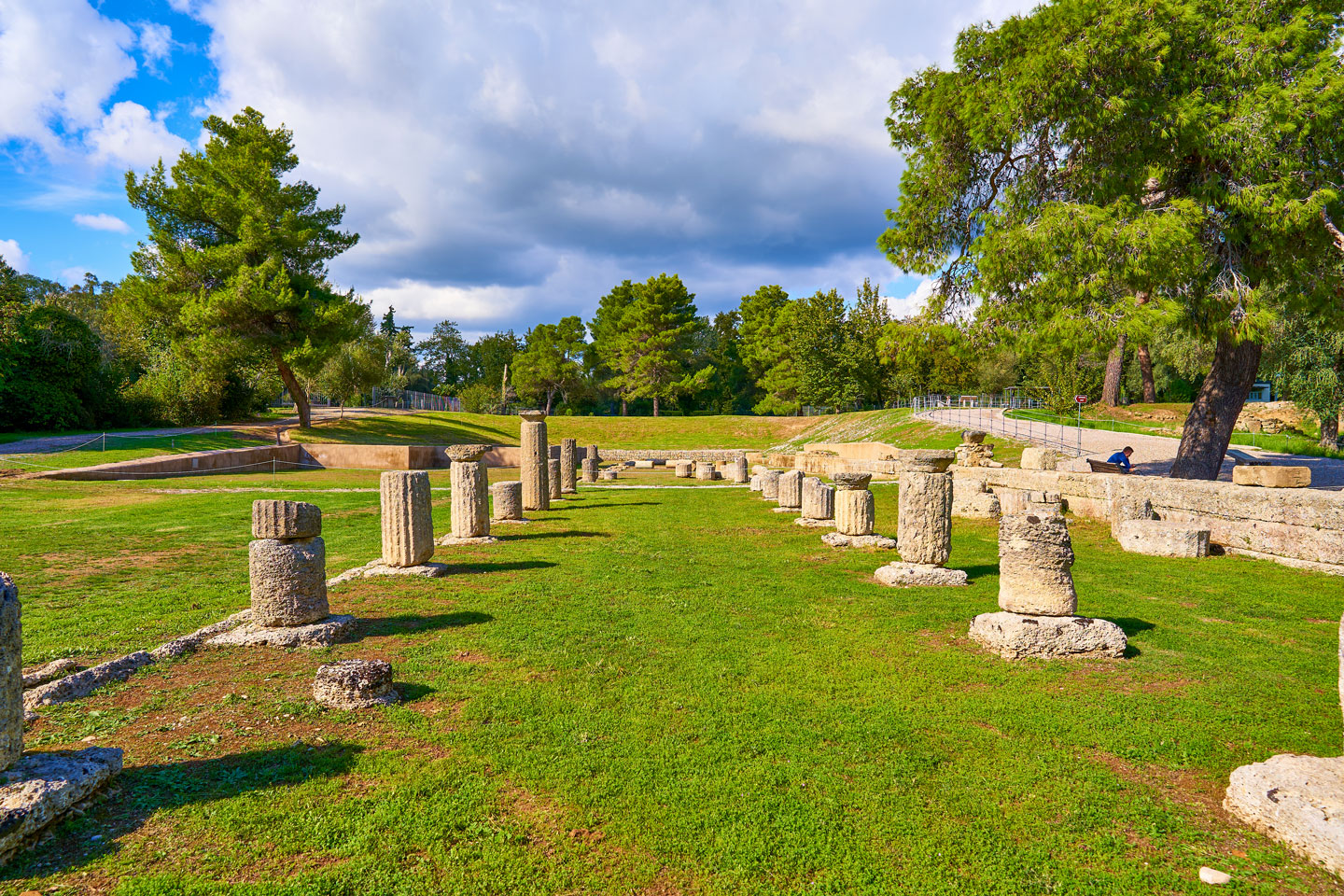 Archaia Olympia, the Archaeological Site of Olympia. The picture shows the remains of the Gymnasium of Ancient Olympia. The ancient Olympic Games were the forerunners of the modern Olympic Games, a series of athletic competitions among representatives of Greek city-states. The games were held at the Panhellenic religious sanctuary of Olympia.
Photo: George E. Koronaios
Archaia Olympia, the Archaeological Site of Olympia. The picture shows the remains of the Gymnasium of Ancient Olympia. The ancient Olympic Games were the forerunners of the modern Olympic Games, a series of athletic competitions among representatives of Greek city-states. The games were held at the Panhellenic religious sanctuary of Olympia.
Photo: George E. Koronaios
Greece has a Mediterranean climate, with wet winters and hot, dry summers. The climate supports the cultivation of olives, grapes and grains, such as wheat and barley, which were among the staple foods of the ancient Greeks.
Cities
Greece's largest cities are Athens and its suburb municipalities, Thessaloniki and its suburbs, Patras, Piraeus, Heraklion, Larissa, Volos, Ioannina, Chalcis, Trikala and Alexandroupoli.
Transport
Buses and ferries are the most important means of transportation in the country. The
Hellenic Railways Organization (OSE) is the Greek national railroad company that owns, maintains and operates all railroad infrastructure in Greece, except the rapid transit lines in Athens. The Greek railway is connected to the rest of
Europe by the
Orient-East Med Corridor via Bulgaria.
Airports
The ten busiest Greek airports are
Athens International Airport "Eleftherios Venizelos" (
IATA Code: ATH),
Heraklion International Airport "Nikos Kazantzakis" (IATA Code: HER),
Thessaloniki International Airport "Makedonia" (IATA Code: SKG),
Rhodes Island International Airport "Diagoras" (IATA Code: RHO),
Corfu Island International Airport "Ioannis Kapodistrias" (IATA Code: CFU), Chania International Airport "Ioannis Daskalogiannis" (IATA Code: CHQ) on
Crete island,
Kos Island International Airport "Hippocrates" (IATA Code: KGS),
Santorini International Airport "Zefiros" (IATA Code: JTR),
Zakynthos Island International Airport "Dionisios Solomos" (IATA Code: ZTH) and
Mykonos Island National Airport "Dilos" (IATA Code: JMK).
List of the Greek islands shown on the map:
The largest Greek islands are Crete, Euboea (Evia), Lesbos, Rhodes and Chíos.
Islands in the Aegean Sea
Sporades
Alonnisos, Skiathos, Skopelos and Skyros.
Cyclades
Amorgos, Anafi, Andros, Delos, Folegandros, KeaIos, Kythnos, Milos, Mykonos, Naxos, Paros, Santorini (Thera), Serifos, Sifnos, Sikinos, Syros, and Tinos.
Dodecanese
Astypalaia, Kalymnos, Karpathos, Kasos, Kos, Leros, Lipsi, Nisyros, Patmos, Rhodes, Symi, and Tilos.
North Aegean Islands
Major Greek islands in the North Aegean are Agios Efstratios (Saint Eustratius), Lemnos, Samothrace and Thasos.
East Aegean Islands
Major Greek islands in the East Aegean are Chios (Scio), Fournoi, Ikaria, Lesbos, Psara and Samos.
Saronic Islands:
The major Saronic islands are Aegina, Hydra, Poros, Salamis and Spetses.
Islands in the Ionian Sea
Major Greek islands in the Ionian Sea are Corfu (Kerkyra), Ithaca, Kefalonia, Lefkada, Paxi and Zakynthos. The Greek islands of Kythera and Antikythera are located to the south of Peloponnese, the large peninsula located at the southern tip of the mainland.
A to Z List of Greek cities and municipalities shown on the map:
Agios Nikolaos, Agrinio, Aigio, Alexandroupoli, Amaliada, Amfissa, Archaia, Areopoli, Argos, Argostoli, Arta, Athens, Chalcis, Chania, Chios, Corfu, Corinth, Delphi, Diakopto, Domokos, Drama, Edessa, Elati, Ermoupoli, Faliraki, Filiatra, Florina, Gennadi, Gianitsa, Grevena, Gytheio, Heraklion, Ierapetra, Igoumenitsa, Ioannina, Kalamata, Kalambaka, Kalavryta, Kardamaina, Karditsa, Karpathos, Karpenisi, Karyes, Kassandra, Kastoria, Katerini, Kavala, Kilkis, Komotini, Kos, Kozani, Lamia, Larissa, Lefkada, Lindos, Livadia, Marathon, Megara, Messolongi, Methoni, Monemvasia, Mykines, Myrina, Mytilene, Nafplio, Neapoli Voion, Nikiti, Nydri, Olympia, Orestiada, Orestiada, Patras, Pavliani, Pilos, Piraeus, Plakias, Polygyros, Preveza, Ptolemaida, Pyrgos, Rethymno, Rhodes, Salamina, Samos, Sarti, Serres, Sidari, Sitia, Sparta, Stylida, Thebes, Thermi, Thessaloniki, Tirnavos, Trikala, Tripoli, Veria, Volos, Xanthi and Zakinthos.
Advertisements: