More about Myanmar
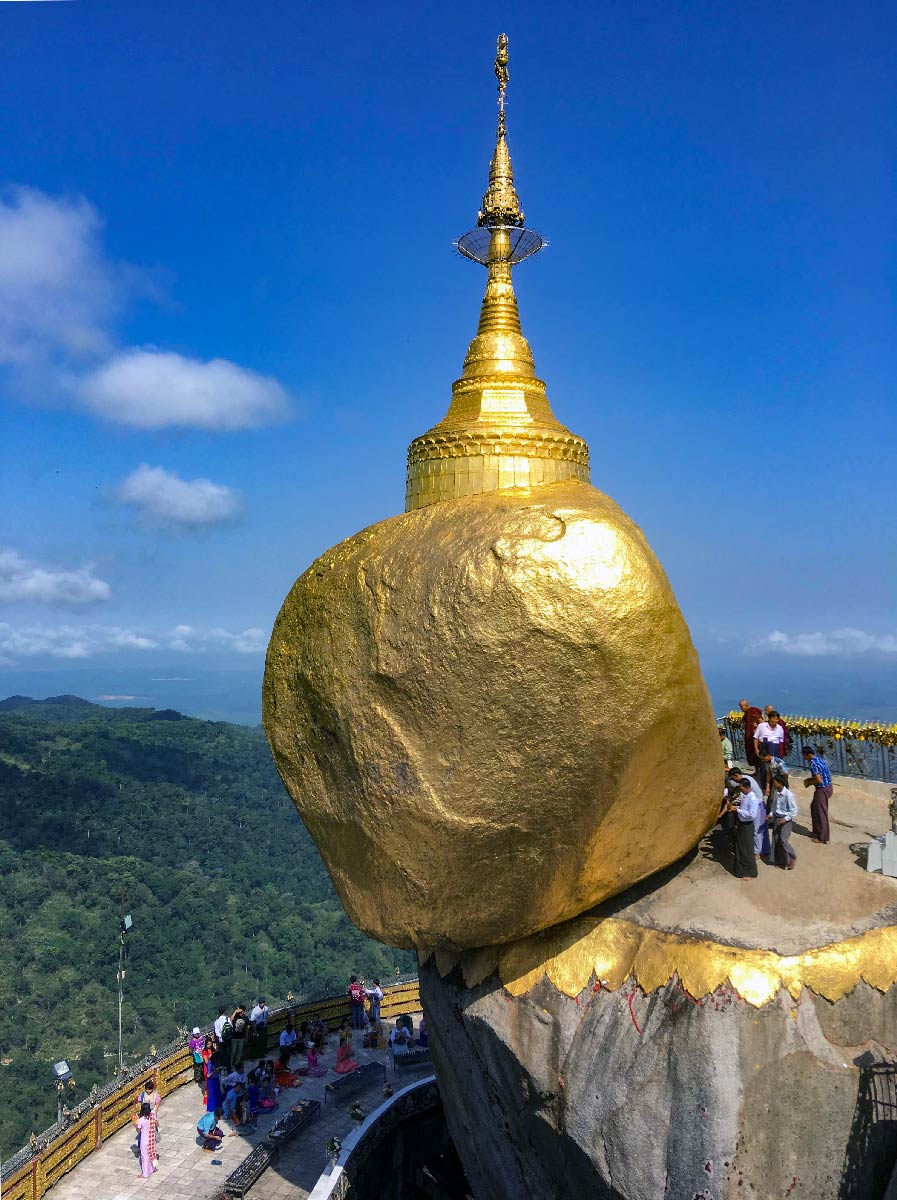 The famous Golden Rock in Mon State is the third most important Buddhist pilgrimage site in Burma after the Shwedagon Pagoda in Yangon and the Mahamuni Buddha Temple in Mandalay.
Photo: Christophe95
The famous Golden Rock in Mon State is the third most important Buddhist pilgrimage site in Burma after the Shwedagon Pagoda in Yangon and the Mahamuni Buddha Temple in Mandalay.
Photo: Christophe95
The landscape of Myanmar slopes gradually from north to south, from an altitude of 5,881 m at Mount Hkakabo (the country's highest peak) in the far north to sea level in the coastal areas in the south. In the west, the Indo-Burman Ranges form a natural barrier between Myanmar and India. In the far north of the country are the mountainous areas of the foothills of the Himalayas, the Kachin Hills, the Kumon Range and the Hengduan (Gaoligong) mountains. The region is home to the country's highest mountains, the Hkakabo Razi (5,881 m) and Mt. Ganlanyazi (Gam laan yazi; 5,834 m)
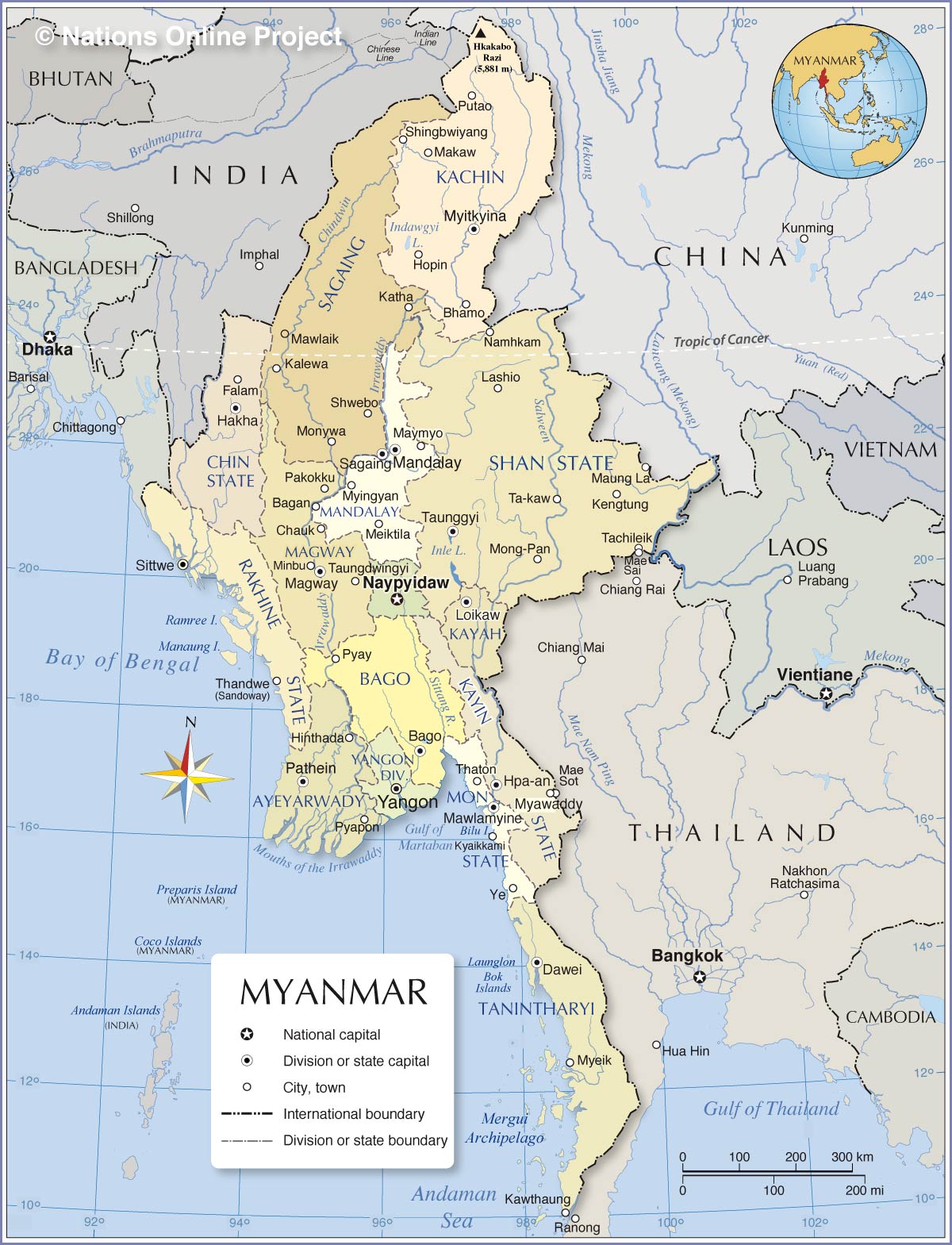
Myanmar's Administrative Divisions
Kachin State
Kachin is Myanmar's northernmost state; it borders the Indian state of Arunachal Pradesh and the Chinese provinces of
Tibet (Xizang) in the north and Yunnan in the east. The landscapes of the northern and the eastern parts of Kachin are dominated by mountainous regions, foothills of the eastern Himalayas. The highest peak is
Hkakabo Razi (5,881 m).
About 45 km north of the state capital Myitkyina is the confluence of the Mali Kha and the N'mai Kha; from there on, the river is called
Irrawaddy. The over 2,100 km long river is something like the lifeline of Myanmar. For centuries, the river was one of the most important waterways in the country.
Indawgyi Lake, one of the largest lakes in Southeast Asia, is located in Mohnyin Township in Kachin.
Kachin's capital is
Myitkyina; other major towns are Putao and Bhamo. The third-largest state in Myanmar is relatively sparsely populated.
Sagaing Region
Sagaing Region is located in the northwestern part of the country. The Pat-kai and Naga Hills form a massive natural boundary between the Sagaing Division and the Indian states of Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland and Manipur. The Chindwin River (The Mighty Chindwin), the main tributary of the Irrawaddy, flows almost entirely through Sagaing and is the most important waterway in the region.
Sagaing Region capital is
Sagaing. The former center of the ancient Sagaing Kingdom is located about 14 km southwest of Mandalay on the opposite bank of the Irrawaddy River. The region's largest city is
Monywa.
Chin State
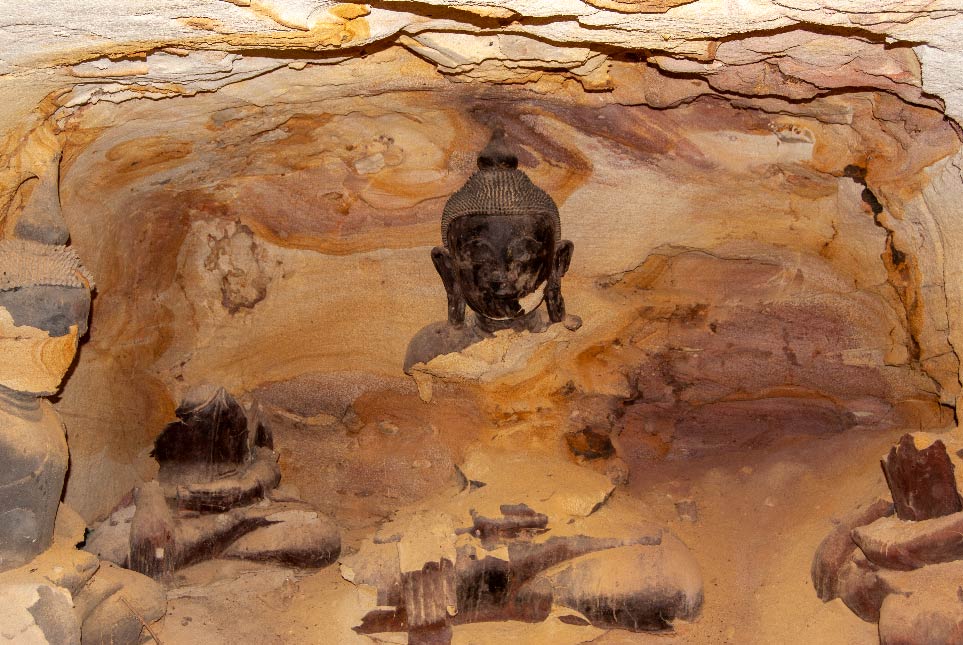 Remains of Buddha statues in Hpo Win Daung cave, Sagaing Region.
Image: kk nationsonline.org
Remains of Buddha statues in Hpo Win Daung cave, Sagaing Region.
Image: kk nationsonline.org
The mountainous Chin State in the west of Myanmar borders Bangladesh and the Indian states of Manipur and Mizoram. The Tiau River forms much of the state's border with India. The Chin Hills dominate the region's landscape; Nat Ma Taung, also known as Mount Victoria (3,053 m), is the highest peak.
Chin State is sparsely populated and is home to various ethnic groups known under the umbrella term Chin (Zo/Mizo/K'Cho); most of them are (Baptist) Christians, which can be attributed to the arrival of American Christian missionaries in the early 19th century.
Spoken languages are dozens of different (unintelligible) Chin language variants, also spoken in neighboring areas of Bangladesh and India. The capital is
Hakha, the second-largest town is Tedim, other notable towns are Mindat and Matupi.
Shan State
Shan is the easternmost and largest state of the country. It borders China in the northeast; a section of the Mekong River defines its border with Laos to the southeast. To the south lies Thailand's Northern Region. There is a land border crossing at Mae Sai (Thailand) - Tachileik (Myanmar). The area around the Burmese, Thai and Lao border triangle is known as the "Golden Triangle."
Shan State covers an area about twice the size of
Ireland or slightly more than the US state of
Georgia. The landscape features hilly to mountainous areas and plateaus, known as Shan hills, with elevations ranging from 300 to 2,600 m (1,000 - 8,700 ft). The highest peak in Shan State is Loi Leng, at 2,673 m. The highland is crossed by the deep gorge of the Salween (Thanlwin) River. The Myitnge River (Nam Tu) drains the northern Shan Plateau and empties into the Ayeyarwady (Irrawaddy).
State capital and largest city is
Taunggyi, located about 20 km northeast of
Inle Lake, a scenic destination and major tourist trap.
Other urban areas of considerable size are Lashio and Kengtung.
Mandalay Region
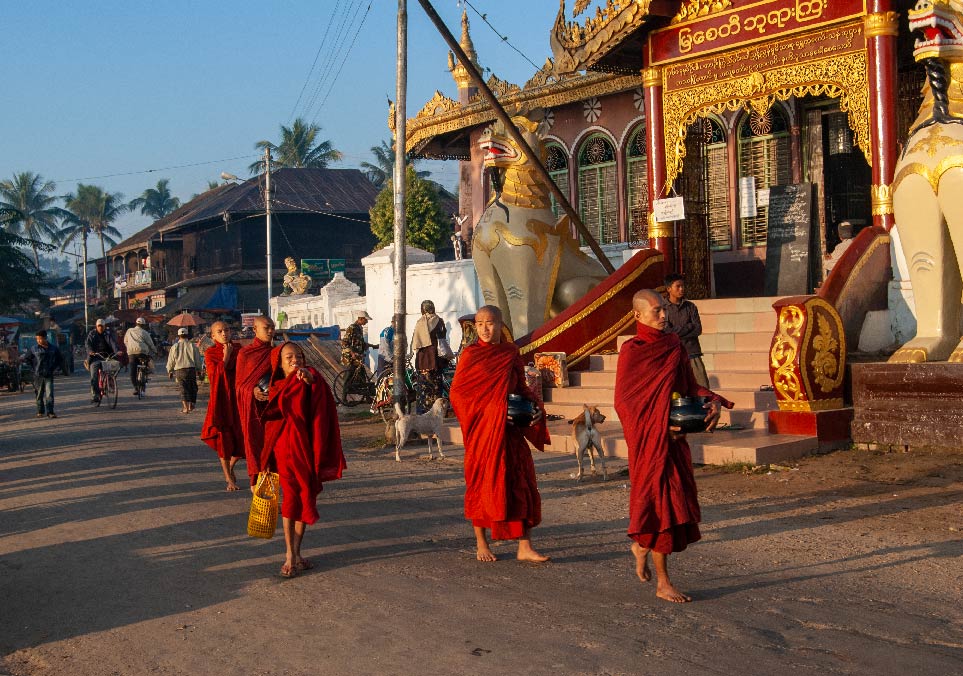 Burmese Buddhist monks collecting alms.
Image: kk nationsonline.org
Burmese Buddhist monks collecting alms.
Image: kk nationsonline.org
The Mandalay Region is located in the center of the country; the Irrawaddy River forms most of its border with the Sagaing Region. The capital and largest city is
Mandalay, Myanmar's second city. It is served by Mandalay International Airport (
IATA: MDL), one of only three international airports in the country.
Mandalay Region is home to some of Myanmar's major tourist attractions. The city of Mandalay itself with the rebuilt Mandalay Palace (the replica is kind of a Burmese Disneyland), the Mahamuni Paya, an important Buddhist pilgrimage site, and the wooden Shwe in bin Monastery.
Mount Popa, an extinct volcano adorned with numerous gilded Nat (spirits) temples and relic sites. And there is
Bagan, the ancient Buddhist temple city with over 2,200 temples and pagodas. When Myanmar opened to tourism in 1992, Bagan was the destination for expensive river cruises. Today, the UNESCO World Heritage Site looks more like a tourist amusement park with balloon rides and pizza restaurants and serves as a backdrop for fashion photos and as a place for mass celebrations of sunsets.
Magway Region
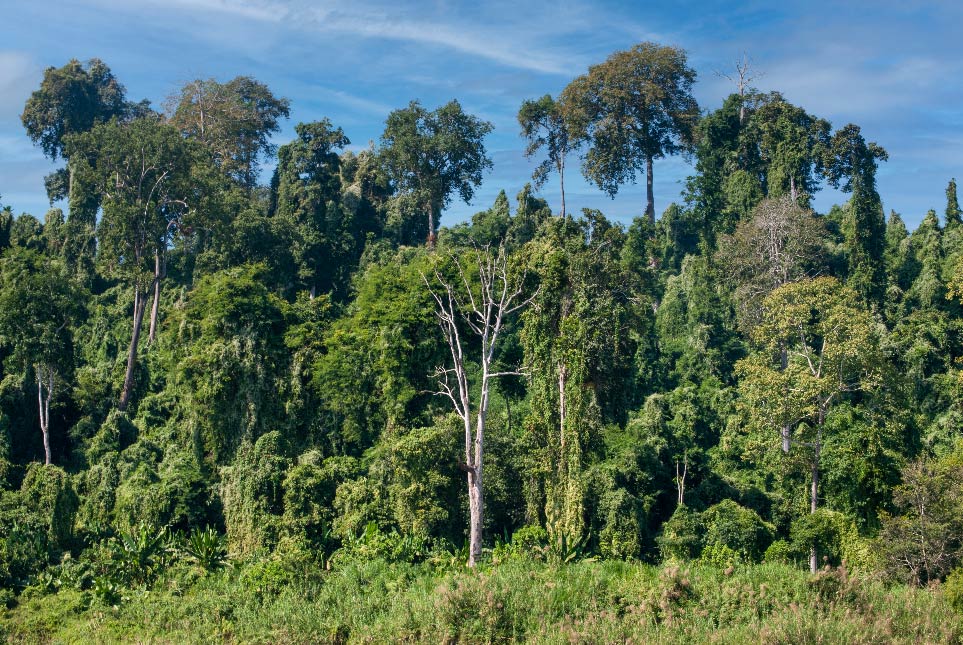 The ancient jungle trees are threatened throughout Myanmar by deforestation and slash and burn.
Image: kk nationsonline.org
The ancient jungle trees are threatened throughout Myanmar by deforestation and slash and burn.
Image: kk nationsonline.org
The Magway Region is situated mainly in the Irrawaddy River valley. The river defines a section of the region's border with the Mandalay Division and flows then through its center. In the west, the Rakhine (Arakan) mountains form most of Magway's borders with the Rakhine and Chin regions. The division capital is
Magway; the largest city is Pakokku. Most of Magway's major towns are located along the Irrawaddy River, such as the oil-producing town of Chauk, which forms an urban center together with Seikphyu. Other river ports are Aunglan, Yenangyaung, Thayet, and Minbu.
Naypyidaw Union Territory
Naypyidaw Union Territory was formerly part of the Mandalay Division. The territory is the location of the country's brand-new artificial administrative capital and the seat of the government of Myanmar.
Nay Pyi Taw is home to the Union Parliament, the Supreme Court, the Presidential Palace and several golf courses. The cityscape is completed by a variety of 4-star hotels, a 20-lane semi-deserted highway, various pagodas, among them, a replica of the Mahabodhi Temple of Bodh Gaya (India), several reservoirs, a water fountain park, a 'general' hospital, Naypyitaw Airport, empty shopping malls, a convention center, and various ministries and military facilities.
Kayah State
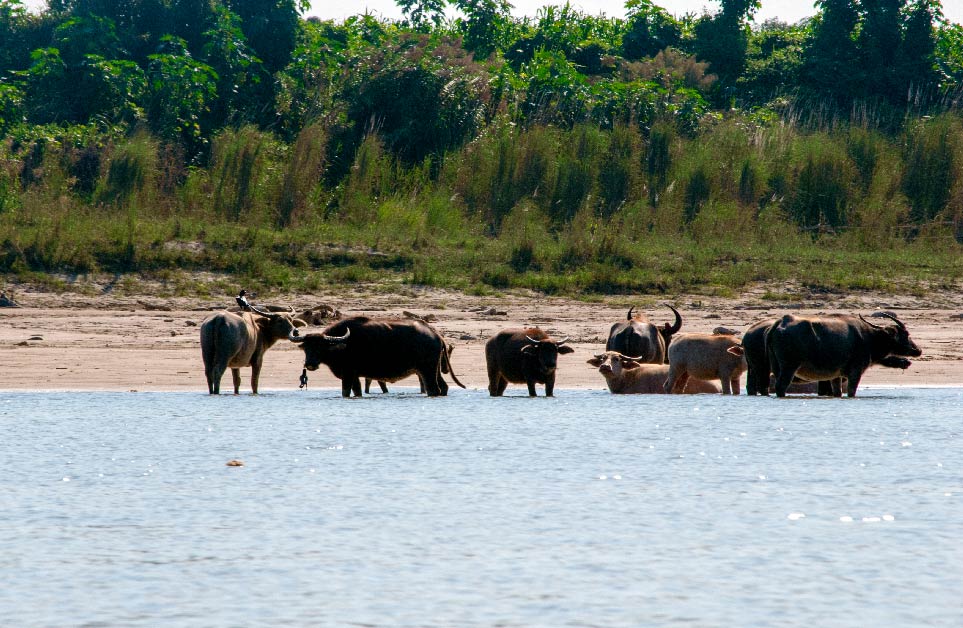 Water buffaloes cool off in the Irrawaddy River.
Image: kk nationsonline.org
Water buffaloes cool off in the Irrawaddy River.
Image: kk nationsonline.org
Small mountainous Kayah State, aka Karenni State, borders Thailand's Mae Hong Son Province in the east. The capital and largest city is
Loikaw. Kayah was originally the homeland of the Kayah people, also known as Karenni or Red Karen. At the time of the British occupation, the Kayah lived in a largely autonomous kingdom, which was incorporated into the Union of Burma in 1947. It is Myanmar's least populous division. The Thanlwin (Thanlyin/Salween) River crosses the state from northeast to southwest.
Rakhine
Rakhine State in the southwest of Myanmar has a coastline on the Bay of Bengal with countless smaller islands, cliffs, sandbanks and bay shoals.
Ramree is the largest island on the Rakhine Coast.
Near the town of
Thandwe is
Ngapali, until now the country's most famous beach. Nearby, Cheduba (Manaung) Island could become the next holiday destination. The capital city of Rakhine is
Sittwe, from there you can take a boat to the medieval town of
Mrauk U.
Bago Region
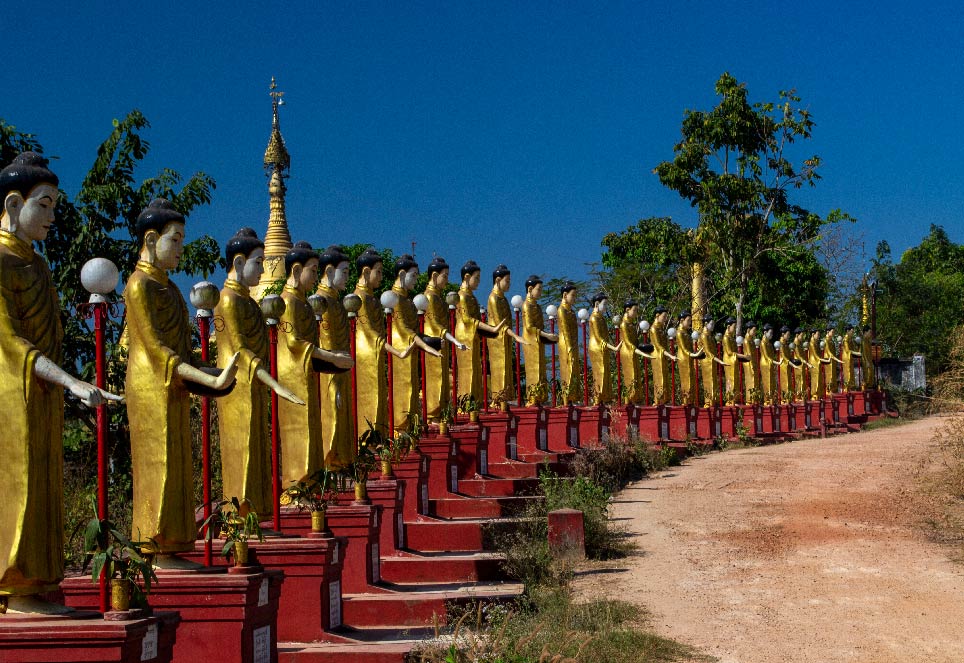 A line of Buddha statues in Bago, Bago Region.
Image: kk nationsonline.org
A line of Buddha statues in Bago, Bago Region.
Image: kk nationsonline.org
The western third of the Bago region in south-central Myanmar (Lower Burma) is predominantly flat. The Pegu (Bago) Range dominates the sparsely populated hilly center. Along the mountains eastern edge runs the new, 586 km long Yangon–Mandalay Expressway, currently the most important transport route in the country that connects Myanmar's largest city Yangon and Mandalay, the second-largest city. Bago's eastern third borders the rugged mountains of the Kayin State. In the south, the region has a 60 km long coastline along the Gulf of Martaban. The capital and principal city is
Bago. Other urban centers are Pyay and Taungoo.
Ayeyarwady Region
The Ayeyarwady Region in the mainland's south is also known as the Delta Region. The coastal region, about half the size of Ireland, lies between the Bay of Bengal and the Gulf of Martaban and refers to the vast estuary of the Irrawaddy (Ayeyarwady), Myanmar's main river. The delta area is known as the "Granary of Burma," the principal crop is rice.
Pathein is the largest city and the capital of the Ayeyarwady Region. In the west, at the Bay of Bengal, there are two popular beach resorts,
Ngwesaung and
Chaungtha Beach. The country's highest deforestation rate threatens the ecosystem of the delta.
[1]
Yangon Region
The relatively small Yangon Division surrounds the former capital Yangon (Rangoon) and borders the Gulf of Martaban. The Yangon/Bago river connects Myanmar's largest city with the Andaman Sea. A mixture of colonial architecture, modern skyscrapers, small-scale industry areas, gilded Buddhist pagodas and noisy, heavy traffic greets the region's visitors.
Kayin State
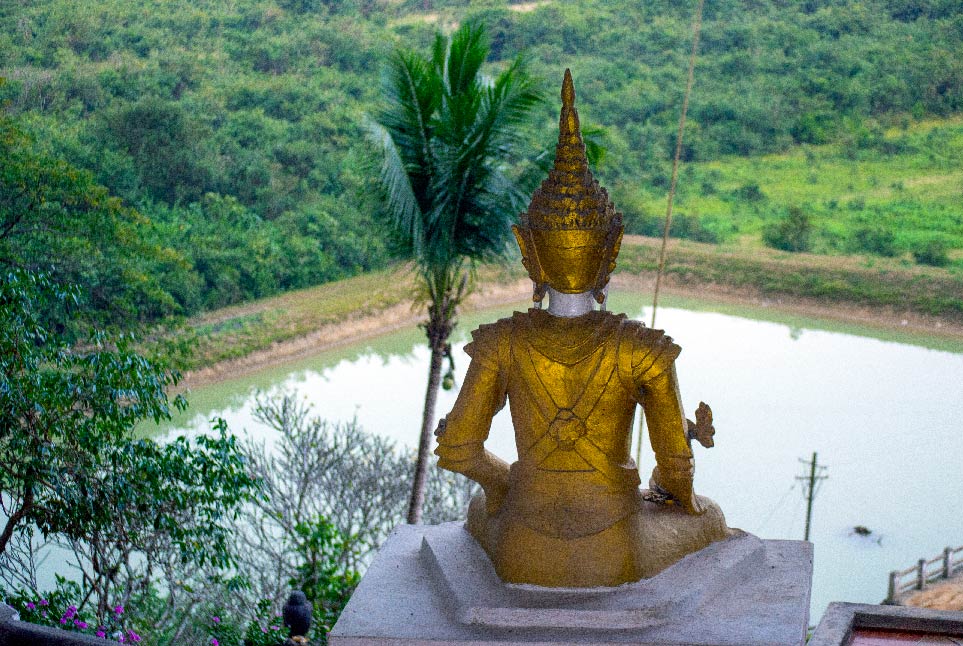 Budhha statue at a water basin, Hpa-an, Kayin State.
Image: kk nationsonline.org
Budhha statue at a water basin, Hpa-an, Kayin State.
Image: kk nationsonline.org
The Kayin State, or Karen State, is home to several ethnic Karen groups such as the Sgaw, the Pwo, the Bwe, and the Paku Karen (Kayin). The mountainous state borders Thailand in the east.
Hpa-An is the capital city. The region is known for its hot springs, mist-shrouded mountains and its many caves, the most visited of which is the huge Sadan Cave south of Hpa-An.
To the west of Kayin is the Myawaddy/Mae Sot border crossing, one of the official road border crossings for foreigners. In the town of Payathonzu in the southeast, there is another border crossing to the Thai province of Kanchanaburi at the Three Pagodas Pass in the Tenasserim Hills.
Mon State
Mon State in the south of the country stretches along the Gulf of Martaban and the Andaman Sea. It is home to Mon people, considered the oldest ethnic group living in present-day Burma.
The Dawna Range in the east forms a natural border between the Mon State and the Kayin State.
State capital is
Mawlamyine, other urban centers are Thaton, Kyaikkami, and Ye. The small town of Kyaikto is famous as the home to the Kyaiktiyo Pagoda, better known as the Golden Rock.
Tanintharyi Region
Tanintharyi Region is Myanmar's southernmost region; it covers the Burmese part of the Malay Peninsula and borders Thailand in the west.
The region's main geographical features are the Andaman Sea and the
Mergui Archipelago to the west, and the
Tenasserim Hills to the east. The region's capital is
Dawei. Other major towns are Bokpyin, Kawthaung, and Myeik. In the far south is the Kawthaung/Ranong land crossing (actually by boat) into Thailand.
Airports
The principal airport of Myanmar is Yangon International Airport (
IATA code: RGN) in Yangon. Mandalay International Airport (IATA: MDL) is the second of only three international airports in all of Myanmar. The other is Nay Pyi Taw International Airport (IATA: NYT). There are regional airports at Bhamo (Banmaw), Dawei, Heho (IATA: HEH), Kalemyo, Mergui, Myitkyina (IATA: MYT), Putao (IATA: PBU) and Sittwe (IATA: AKY).