About Argentina
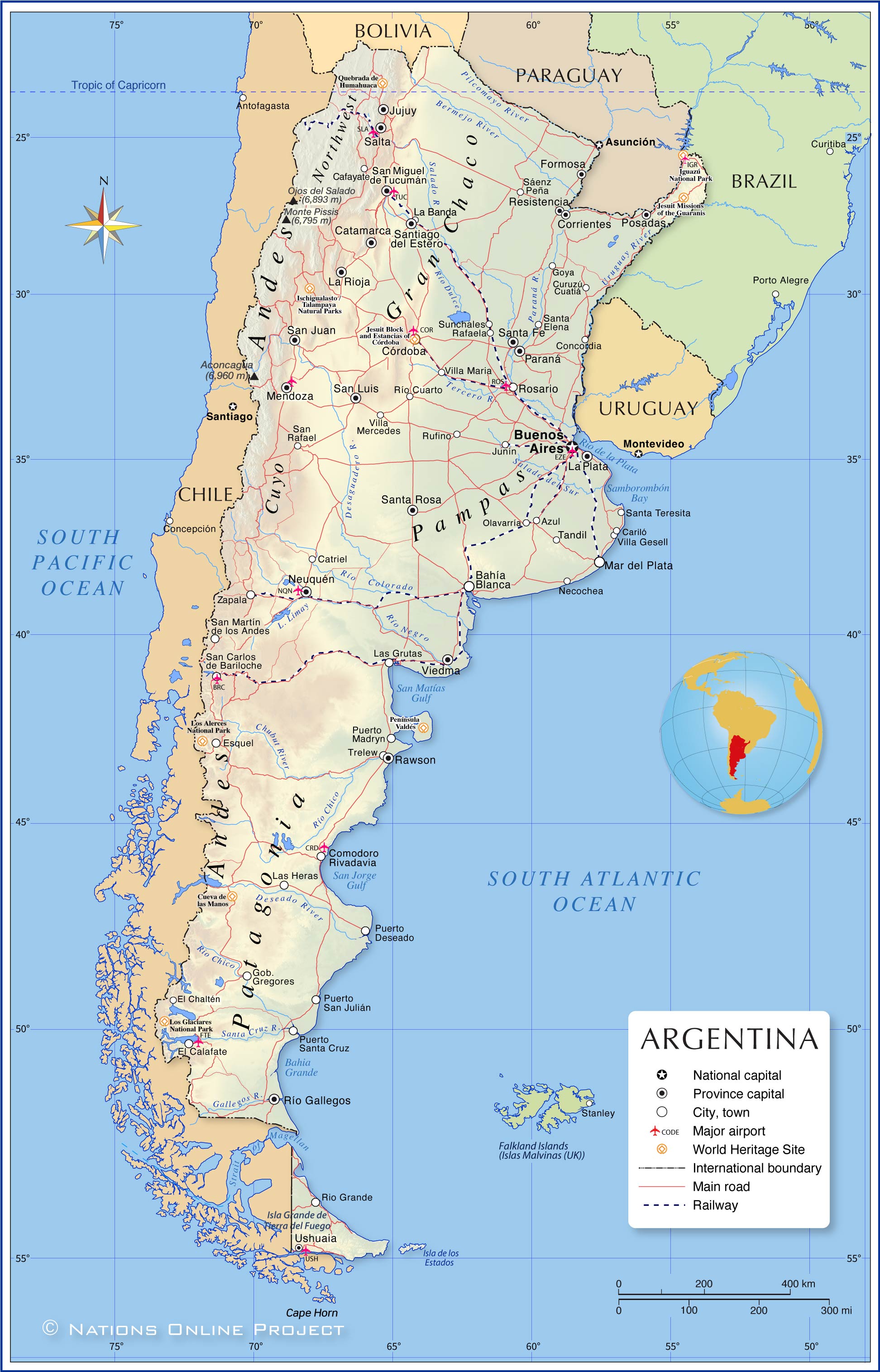
The map shows Argentina, an independent state that occupies a large part of South America's southern portion. With an
area of 2,780,400 km², it is the eighth-largest country in the world and the second-largest country in South America (after
Brazil). In comparison, it is somewhat larger than five times the size of
France or about four times that of the US State of
Texas.
Argentina borders
Chile in the west,
Bolivia and
Paraguay in the north, the
Uruguay River forms sections of its border with
Brazil and all of its border with
Uruguay in the northeast. The southeastern part of Argentina is bounded by the South Atlantic Ocean. The country shares maritime borders with the Falkland Islands (
United Kingdom (The controversial British claim to sovereignty over the Falkland Islands dates back to 1690)). Until Argentina's independence in 1816, the territory was part of the Spanish colonial empire.
Argentina's landscape is characterized by the
Andean Mountains in the west, the wooded and endangered
Gran Chaco in the north, the
Pampas plains in the central-east, the
Cuyo, a mountainous wine-producing region in the central-west, the barren plateau of
Patagonia in the south and the
Tierra del Fuego archipelago in the far south.
Argentina has a
population of 46 million people (in 2022). The capital and largest city is
Buenos Aires. The Official language is Spanish; regional spoken languages are Italian, German, Welsh, Quechua, and Guaraní.
More about Argentina
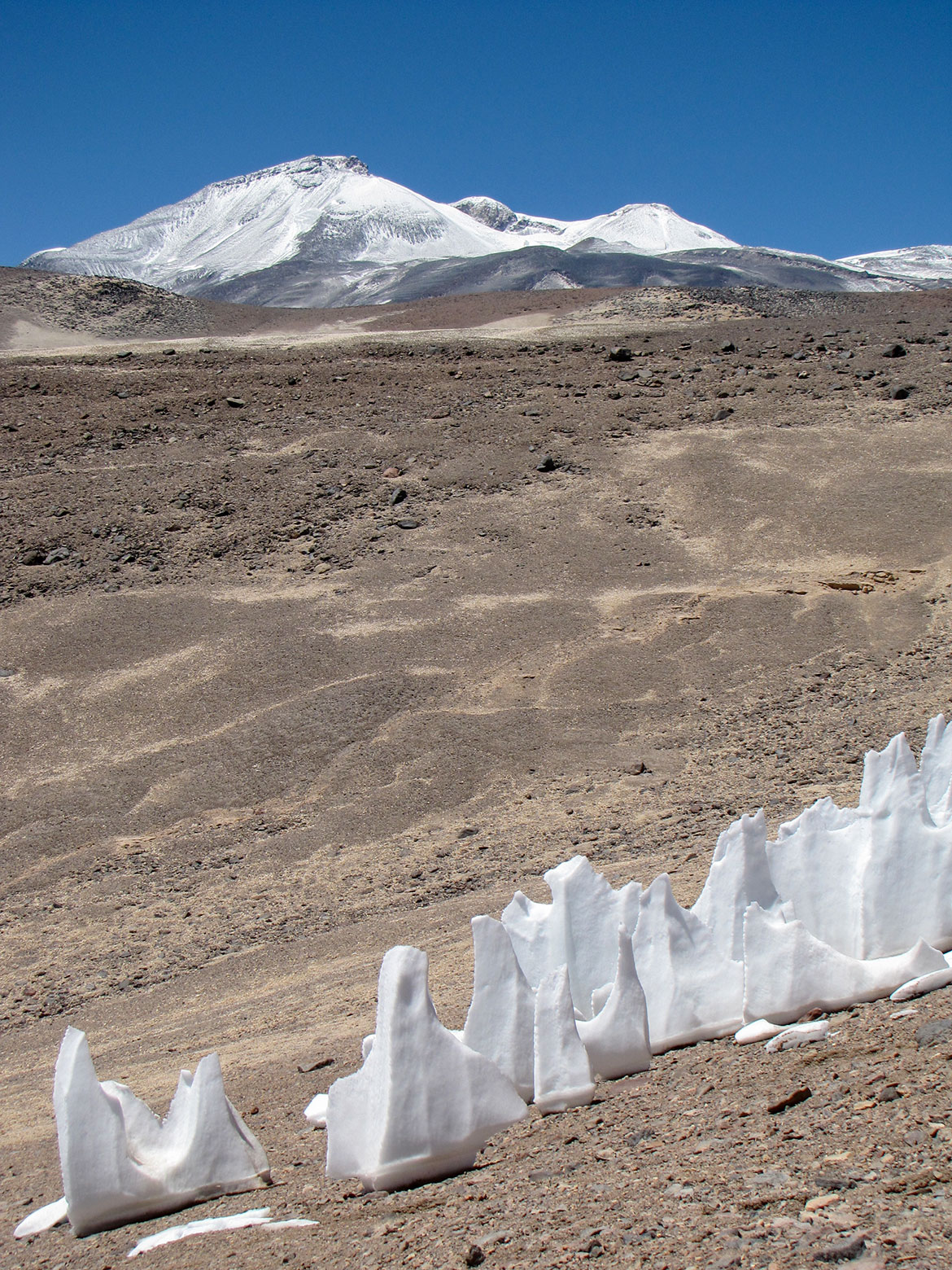 The Ojos del Salado volcano on the Argentine-Chilean border is the highest active volcano in the world at 6,893 meters.
The Ojos del Salado volcano on the Argentine-Chilean border is the highest active volcano in the world at 6,893 meters.
Photo: sergejf
Argentina is the second-largest country in South America after Brazil.
Argentina's major geographic regions are:
- The Andes, the vast mountain range that runs along the western coast of South America.
- The subtropical Northwest, consisting of mountains and fertile valleys, is an important agricultural region with crops such as sugarcane, tobacco, and citrus fruits.
- The Gran Chaco is a vast, sparsely populated region characterized by a hot, semi-arid climate where dry forests and grasslands cover much of the area.
The Gran Chaco is the second largest forest in South America after the Amazon rainforest. It is one of the most deforested areas on earth.
The environmental impact of human activity in the Gran Chaco has been a subject of concern in recent years, with deforestation and land degradation causing significant damage to the ecosystem. [Nature]
- Cuyo is a mountainous area in the central-west, encompassing the provinces of San Juan, San Luis, and Mendoza. Cuyo is an important agricultural region, especially known for its wine production, with the vineyards of Mendoza producing some of the world's finest wines.
- The Pampas is a vast region in central Argentina that stretches from the Atlantic coast to the foothills of the Andes. The area features fertile grasslands, flat terrain and a temperate climate ideal for agriculture. The Pampas is one of the country's most important agricultural regions, growing large quantities of crops such as wheat, corn and soybeans. Cattle farming is also an important industry, producing some of the best beef in the world.
- Patagonia is known for its rugged landscapes, including towering mountains, expansive deserts, and pristine glaciers. The region is home to diverse wildlife, including penguins, sea lions, guanacos, and Andean condors.
- Tierra del Fuego is an archipelago at South America's southernmost tip. The group of islands is separated from the mainland by the Strait of Magellan. It is divided between Chile, to the west, and Argentina, to the east, and includes the main islands of Tierra del Fuego, Navarino, Hoste, and numerous smaller islands.
Mountains
Along its entire western border area with Chile extend the Andes, the longest continental mountain range on earth. Several mountains in the Andes reach heights of over 6000 m. Among them is Aconcagua (6,961 m), the highest peak in the Americas is located in the
Principal Cordillera of the Andes. The country also features the two highest volcanoes on earth,
Ojos del Salado at 6,880 m and
Monte Pissis at 6,795 m.
Rivers
The Rio de la Plata Basin, the water catchment area of the northeastern part of the country, is dominated by the rivers that feed the Río de la Plata, a relatively short river (290 km) that flows into the Atlantic Ocean. The Río de la Plata's principal tributaries are the Pilcomayo, the Bermejo, the Salado, the Paraná, the Paraguay River, and the Uruguay River.
Major rivers in the southern part of Argentina are (from north to south) the Desaguadero River, the Río Colorado, the Río Negro, the Chubut River, Río Chico, the Deseado River, another Río Chico, the Santa Cruz, and the Gallegos River.
Lakes
Major lakes in the country are Lake Buenos Aires, Argentino Lake, Viedma Lake, Lago O'Higgins (Lago San Martin), Lake Gutierrez, and Mar Chiquita Lake.
Salt flats
Lago Salinas Grandes, Lago Salinas de Ambargasta, Salinas Grandes del Noroeste, Salinas Grandes del Sur (Lago Salinas Grandes, Lago Salina, and Lago Salina Santa Ines).
Cities
Buenos Aires is Argentina's capital and largest city, with a population of about 3 million people.
Greater Buenos Aires, with a population of 12 million people, is an urban agglomeration surrounding the capital. It consists of several large cities (also known as Partido), such as La Plata (capital of the province of Buenos Aires), Vicente López, Mar del Plata, Pilar, Merlo, Quilmes, Banfield, José C. Paz, Lanús, to name a few.
Other major
Argentinian cities are Córdoba, Rosario, San Miguel de Tucumán, Salta, Santa Fe (de la Vera Cruz), Corrientes, Resistencia, Posadas, Jujuy (San Salvador de Jujuy), Santiago del Estero, Paraná, Neuquén, Formosa, La Rioja, Comodoro Rivadavia, San Luis, and Catamarca.
Climate
Argentina is a vast country; the extension from north to south is about 3,700 km; its territory offers almost all climate zones in one nation, from tropical areas in the extreme northeast (Misiones) to subtropical regions in the rest of the north and an extensive temperate climate zone to cold climate regions in the south (Patagonia) and in the Andes mountain range.
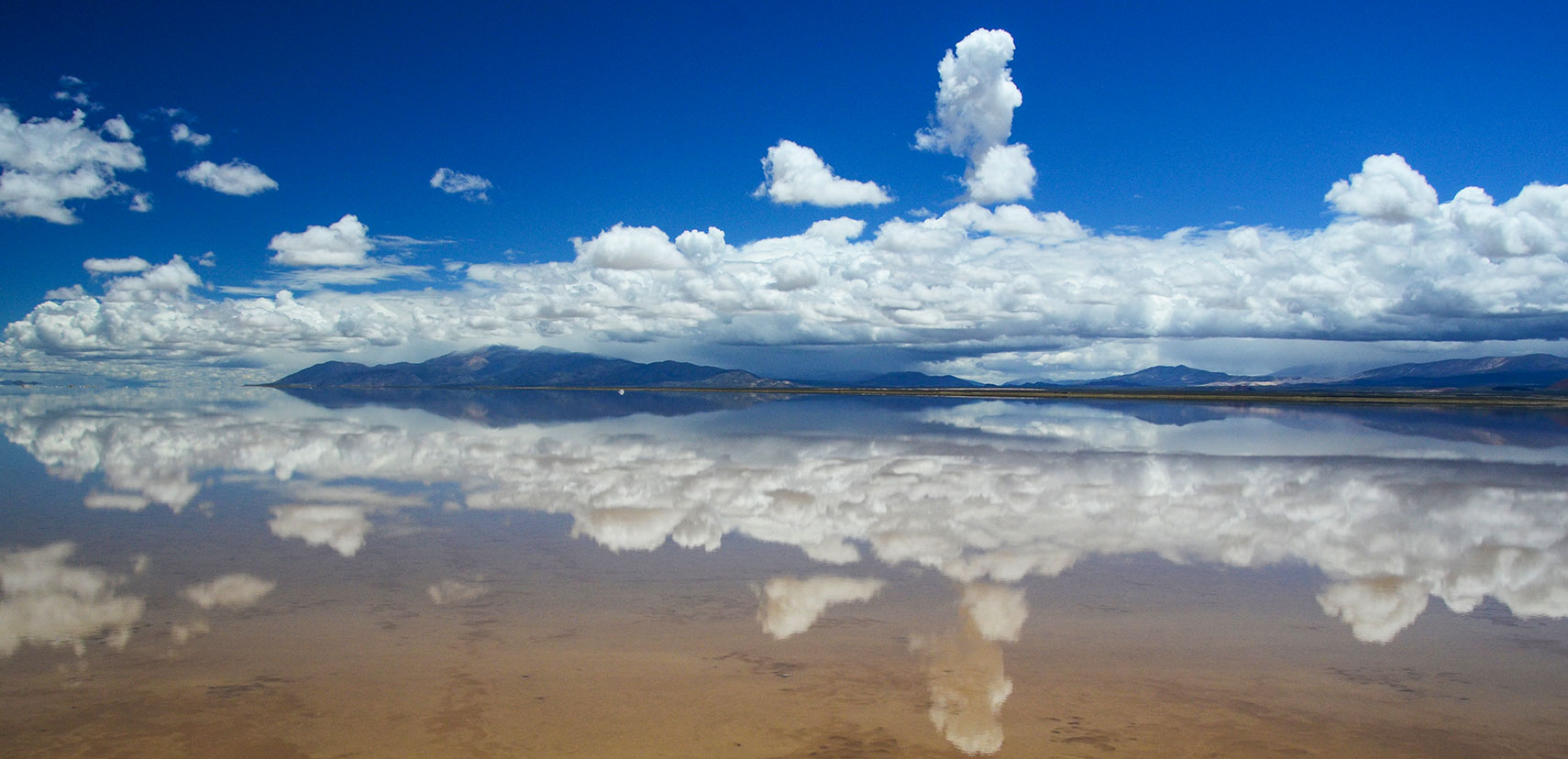 Salinas Grandes after the rain. The salt flat in the Argentinean provinces of Jujuy and Salta in the northwest of Argentina covers an area of 212 km and has an average thickness is 30 cm.
Image: schnoogg
Salinas Grandes after the rain. The salt flat in the Argentinean provinces of Jujuy and Salta in the northwest of Argentina covers an area of 212 km and has an average thickness is 30 cm.
Image: schnoogg
The map shows the location of the following cities, towns:
Azul, Bahía Blanca, Buenos Aires, Cafayate, Cariló, Catriel, Comodoro Rivadavia, Concordia, Córdoba, Corrientes, Cuatiá, Curuzú, El Calafate, El Chaltén, Esquel, Formosa, Gobernador Gregores, Goya, Junín, La Banda, La Plata, La Rioja, Las Grutas, Las Heras, Mar del Plata, Mendoza, Necochea, Neuquén, Olavarría, Paraná, Posadas, Puerto Deseado, Puerto Madryn, Puerto San Julián, Puerto Santa Cruz, Rafaela, Rawson, Resistencia, Río Cuarto, Río Gallegos, Rio Grande, Rosario, Rufino, Sáenz Peña, Salta, San Carlos de Bariloche, San Fernando del Valle de Catamarca, San Juan, San Luis, San Martín de los Andes, San Miguel de Tucumán, San Rafael, San Salvador de Jujuy, Santa Elena, Santa Fe de la Vera Cruz, Santa Rosa, Santa Teresita, Santiago del Estero, Sunchales, Tandil, Trelew, Ushuaia, Viedma, Villa Gesell, Villa Maria, Villa Mercedes, and Zapala.
Advertisements:



 Map of Argentina
Map of Argentina
