Extreme points of Earth and other fun facts
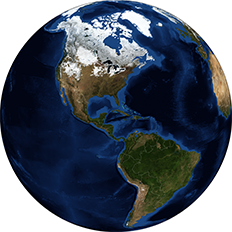
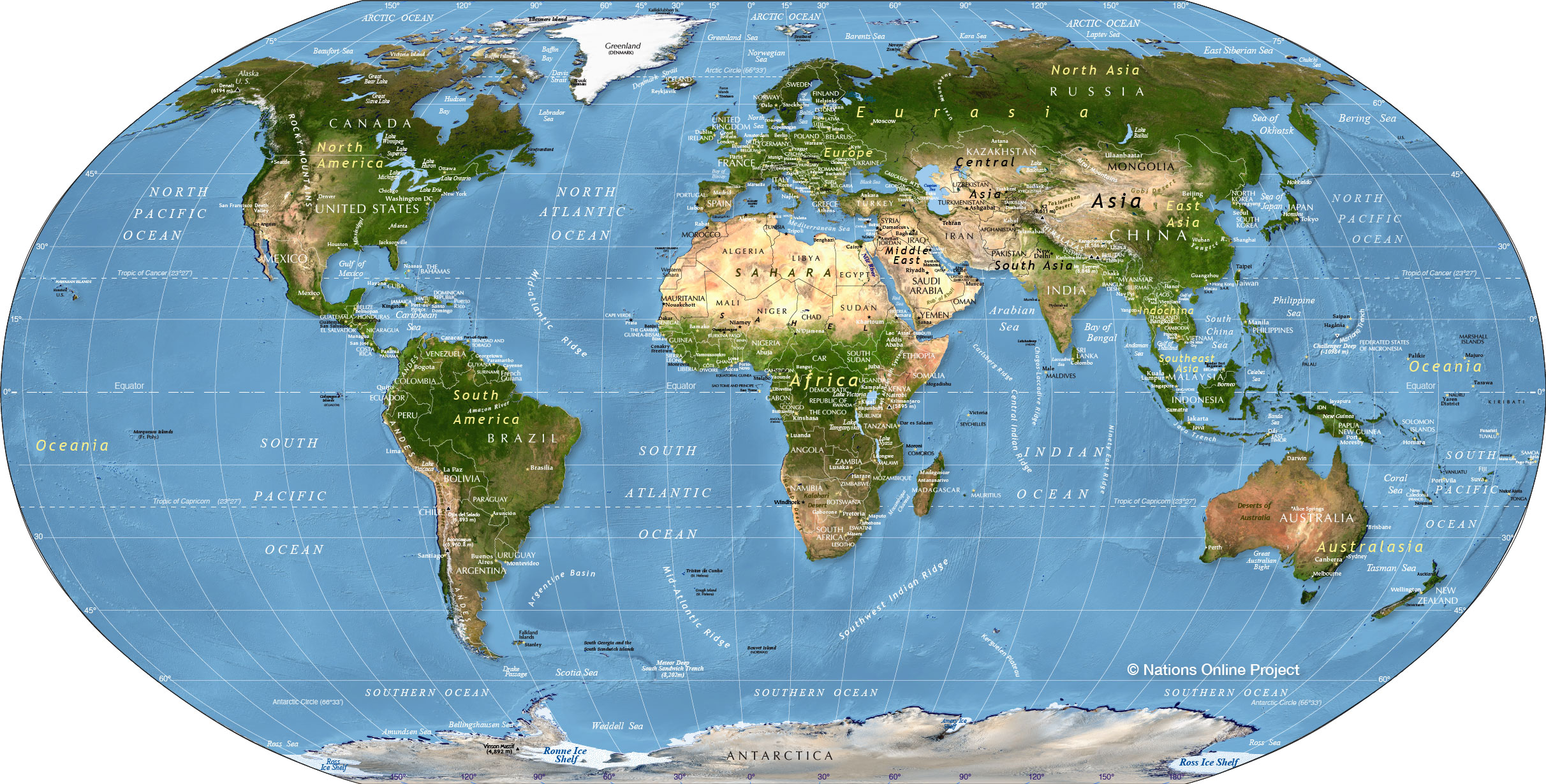
The map shows various extreme points and other important features of the Earth, such as continents, oceans and large islands, deserts, mountains, countries, and capital cities.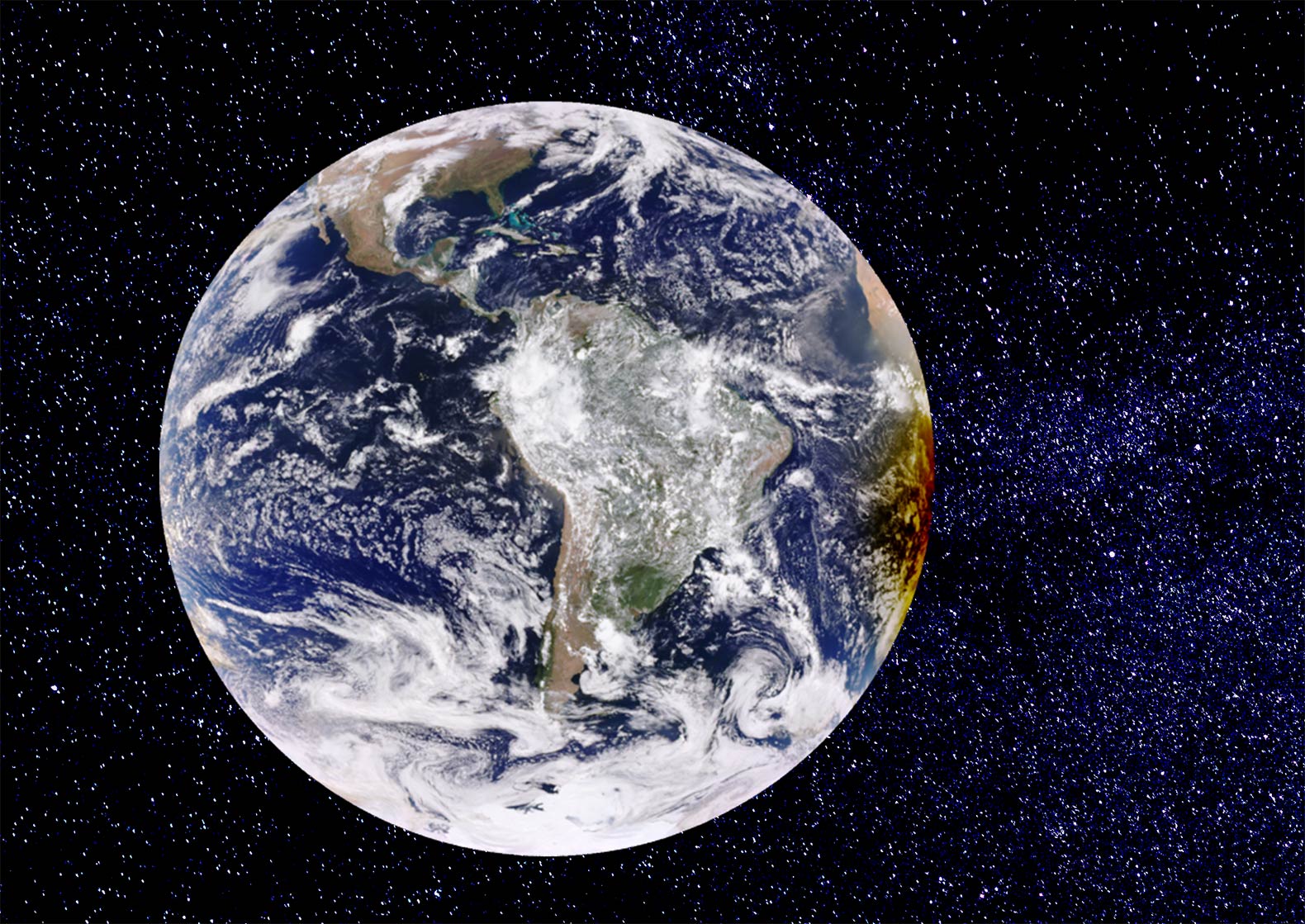  The surface of the Western Hemisphere of the Earth with South America in the center and Antarctica at the bottom. On the right side of the globe a partial solar eclipse is visible, which occurs when a part of the Earth gets into a shadow cast by the moon. Image: NASA - Earth Polychromatic Imaging Camera
The surface of the Western Hemisphere of the Earth with South America in the center and Antarctica at the bottom. On the right side of the globe a partial solar eclipse is visible, which occurs when a part of the Earth gets into a shadow cast by the moon. Image: NASA - Earth Polychromatic Imaging Camera The total area of the earth's surface (land and water) is slightly more than 510 million km² at sea level (100%).
Approximately 360 million km² are water, the salty liquid between the dry land (almost 71%).
The rest, about 29% of the planet's surface, is dry land, rock, stones, sand, mountains, deserts, rivers and lakes, arable land, etc. The total land area, including Antarctica, is about 150 million km².
North and South The northernmost point on Earth is the Geographic
North Pole, where the northern end of Earth's axis of rotation meets the surface on the ice of the Arctic Ocean.
The northernmost
land on Earth is the northern beach of
Kaffeklubben Island, a rocky islet less than 1 km north of Greenland's coast. Nearby Stray Dog West Island might also be a candidate for the northernmost point on land (to be confirmed).
The southernmost point on Earth is the geographic
South Pole. The southern end of the earth's axis is located at the center of the Southern Hemisphere in
Antarctica.
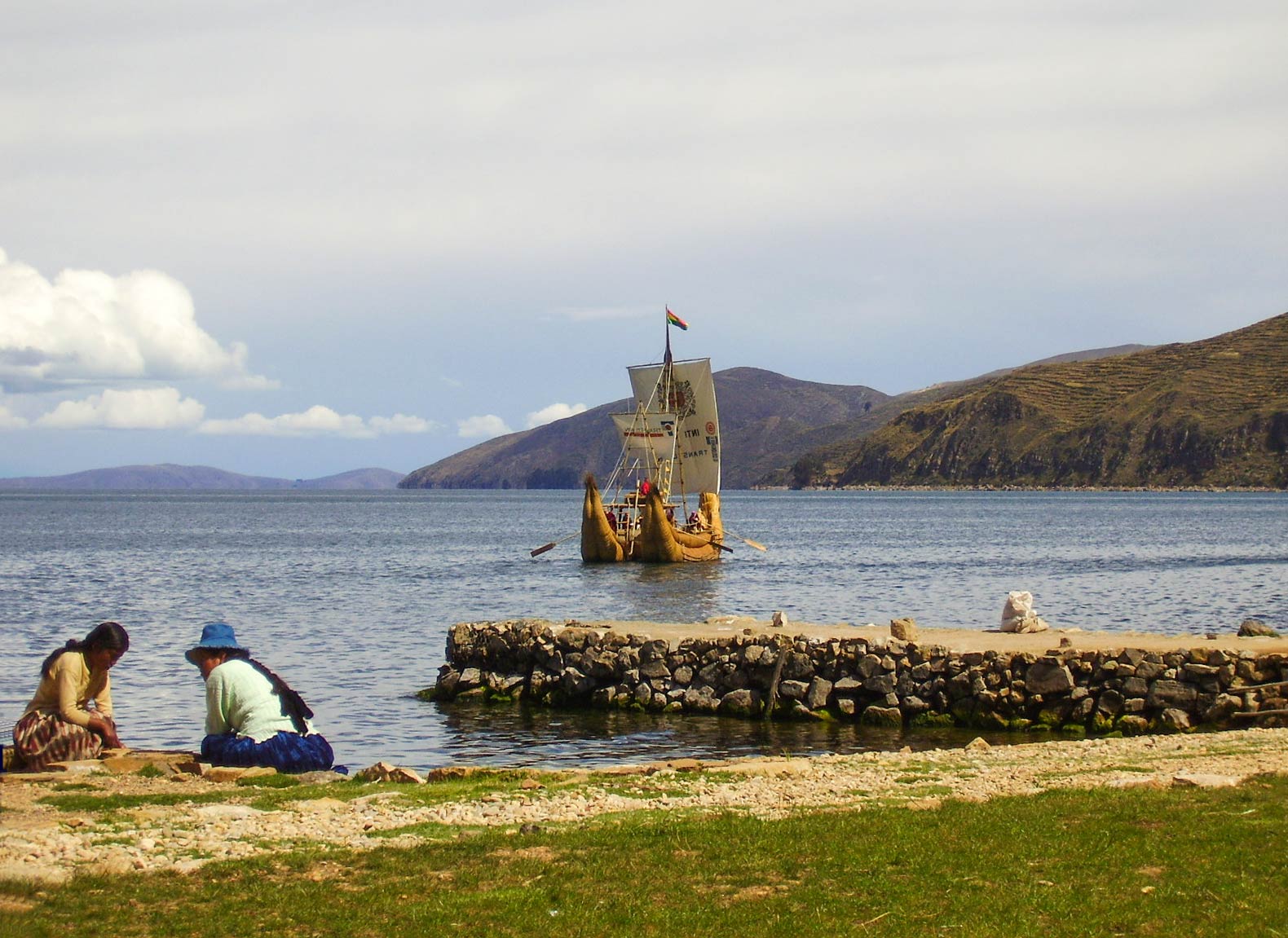 A traditional totora reed raft on Lake Titicaca, seen from Sun Island, Bolivia. Lake Titicaca is the largest lake in South America and known as the "highest navigable lake" in the world. Image: Germarquezm
A traditional totora reed raft on Lake Titicaca, seen from Sun Island, Bolivia. Lake Titicaca is the largest lake in South America and known as the "highest navigable lake" in the world. Image: Germarquezm The highest point on Earth, measured from sea level, is the summit of
Mount Everest. The mountain, also known as Chomolungma, peaks at 8,848 m (29,029 ft; its snow-ice cover included). The Earth's highest mountain is located in the Himalayan Range on the border of
Nepal and
China.
The second-highest mountain on the planet with 8,611 m (28,251 ft) is
K2, located in the northwestern Karakoram Range on the border between
Pakistan and China.
The third-highest mountain in the world is
Kangchenjunga at 8,586 m (28,169 ft) on the
India–Nepal border.
The highest self-made mountain on Earth is
Ojos del Salado at 6,893 m (22,615 ft), an active volcano on the border shared by
Chile and
Argentina.
The
Denali in
Alaska is with 6,190 m (20,300 ft) the highest mountain of the United States and North America.
The highest peak in Antarctica, at 4,892 m (16,050 ft), is the
Vinson Massif.
The highest navigable lake is
Lake Titicaca. The biggest lake in South America is located in the Andes at an elevation of 3,812 m. 27 rivers feed Lake Titicaca; the border between Bolivia and Peru runs through the lake.
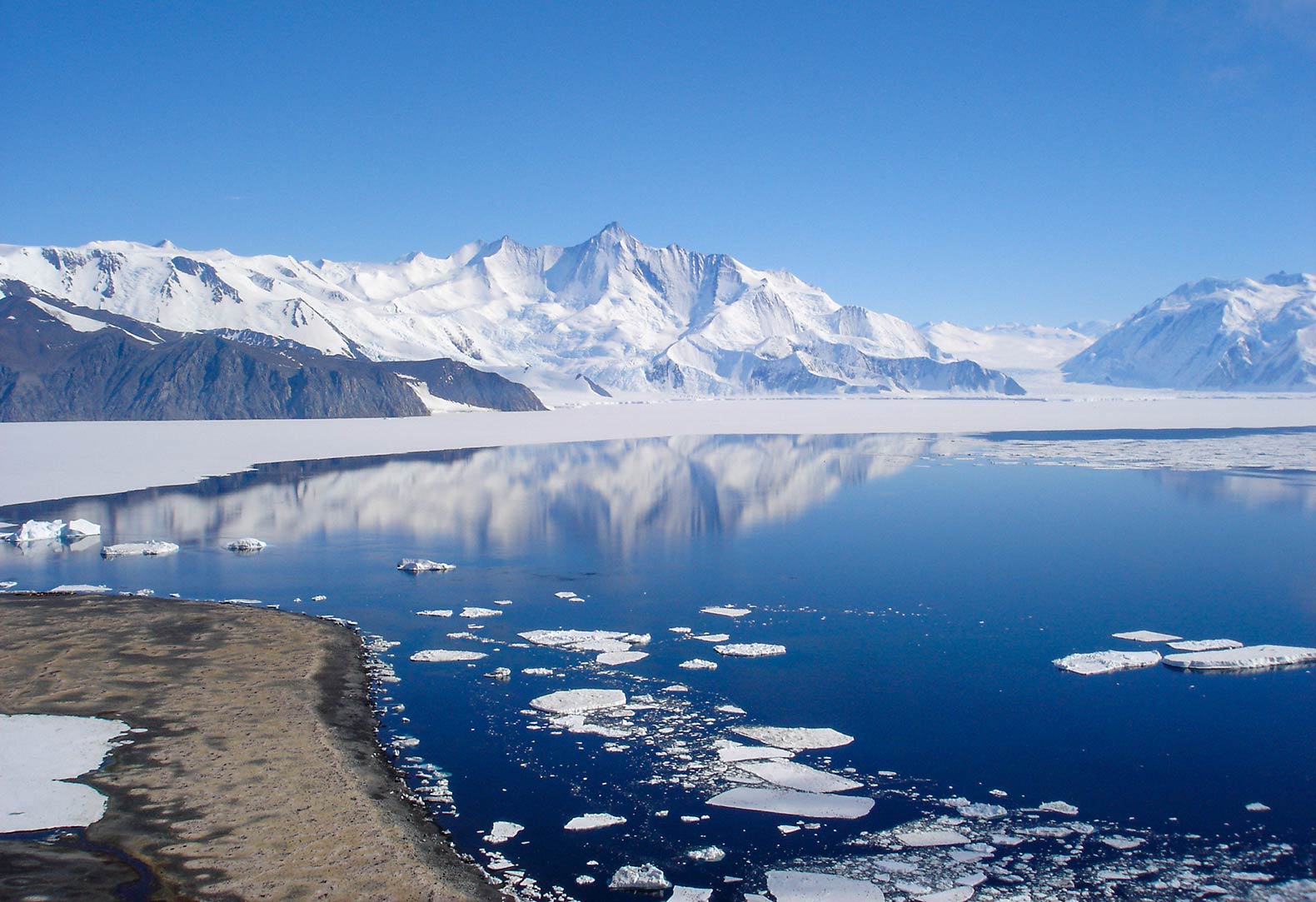 The Southern Ocean surrounds the south polar region, the Antarctic. View of Mount Herschel (3,335 m) in Victoria Land of Antarctica, seen from Cape Hallett. Image: Andrew Mandemaker
The Southern Ocean surrounds the south polar region, the Antarctic. View of Mount Herschel (3,335 m) in Victoria Land of Antarctica, seen from Cape Hallett. Image: Andrew Mandemaker How many oceans are there? In fact, there is only one ocean, a large continuous body of water with relatively free exchange (currents) between its parts.
The major oceanic divisions are known as
1. The
Pacific Ocean is, with an area of approximately 165 million km², the largest body of water; it lies between the Americas (North and South America) on the east and Asia and Australasia on the west. It is divided by the equator into the North Pacific and the South Pacific oceans. Its northern and southern boundaries are the two polar circles.
2. The
Atlantic Ocean, the world's second-largest ocean with an area of almost 80 million km², lies between the Americas on the west and Europe and Africa on the east. Its boundaries are the Arctic Circle and the Antarctic Circle and the meridians through Cape Horn (the southern end of South America) in the west, and Cape Agulhas (the southern tip of the African continent) in the east. The equator divides the ocean into the North Atlantic and the South Atlantic oceans. The
Mid-Atlantic Ridge, a massive, mostly submerged mountain range and the largest geological formation on Earth, runs from north to south through the Atlantic Ocean.
[1] 3. The
Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the five oceans; it covers about 70.5 million km². It is bounded to the north by the Arabian Sea, the Indian subcontinent, and the Bay of Bengal, to the west by the African mainland and the 20th meridian east, to the west by the Indochinese Peninsula, the Indonesian archipelago, and Australia. Its southern boundary is, depending on the definition, the Southern Ocean or Antarctica. The four main access waterways to the Indian Ocean are the Suez Canal in Egypt and the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait, at the southern end of the Red Sea, between Djibouti and Yemen, the Strait of Hormuz between Iran and Oman and the Strait of Malacca between Sumatra (Indonesia) and Peninsular Malaysia.
4. The
Southern Ocean, also (formerly) named Antarctic Ocean, is the sea surrounding Antarctica. The ocean covers an area of about 20 million km², more than twice the size of the US, and is delimited by the 60th parallel south, the latitude where the Antarctic Territory begins.
5. The ice of the
Arctic Ocean forms the region known as the North Pole. It is the smallest of the five principal oceans, with an area of 14 million km². The Arctic Ocean is located in the Northern Hemisphere and is bounded in the south by the 60th parallel north.
 Pelagic Zones of the Ocean. The Hadal Zone or hadopelagic zone is at the bottom.
Pelagic Zones of the Ocean. The Hadal Zone or hadopelagic zone is at the bottom. The probably lowest known natural point is
Vityaz Deep 1, at the bottom of the Mariana Trench, at -11,034 m (-36,201 ft) below sea level. The depth was measured by the Russian research vessel Vityaz in 1957 but never confirmed.
Among the candidates for the deepest known point on the Earth's seabed is the
Challenger Deep, which lies in the Hadal Zone of the Mariana Trench in the Pacific Ocean at nearly -11,000 m (-36,090 ft).
[2] The deepest point in the
Southern Ocean at 8,200 m (26,900 ft) below sea level is known as the
Meteor Deep, located at the eastern edge of the Scotia Sea in the Hadal Zone of the South Sandwich Trench.
The depth specifications are not definitive. Accurate measurement of the depth of the deep sea continues to be a challenge and has hardly been achieved so far.
[3] The lowest point on the land and the lowest tourist place on Earth that you can visit is the shore of the
Dead Sea, 432.65 m (1,419 ft) below sea level. The lake is shared by Israel, Palestine, and Jordan.
The Badwater Basin in the
Death Valley is the lowest point in North America at 86 m (282 feet) below sea level.
Among the deepest points on the earth's surface, not covered by water, is the ice-covered
Bentley Subglacial Trench. The trench is located in western Antarctica and has a depth of 2,555 meters (8,382 ft) below sea level.
Largest Islands The top-ten of the largest islands on the planet are:
1. Greenland (part of the Danish Realm), 2. New Guinea (shared by Indonesia and Papua New Guinea), 3. Borneo (shared by Brunei, Indonesia, and Malaysia), 4. Madagascar (Madagascar, main island) 5. Baffin Island (Canada) 6. Sumatra (Indonesia) 7. Honshu (Japan), 8. Victoria Island (Canada) 9. Great Britain (United Kingdom) 10. Ellesmere Island (Canada).
The most populous island with 145 million inhabitants is Java (Indonesia), more than half of the nation's population.
The largest peninsula is the
Arabian Peninsula in the Middle East.
 Volcanic Mo'orea, the Magical Island, lies northwest of Tahiti in remote French Polynesia. Image: Matthew Dillon
Volcanic Mo'orea, the Magical Island, lies northwest of Tahiti in remote French Polynesia. Image: Matthew Dillon Among the most remote inhabited locations on Earth is
Tristan da Cunha, a group of volcanic islands in the South Atlantic Ocean. The small archipelago is a constituent part of Saint Helena, a British Overseas Territory, and lies 2,780 km west of
Cape Town, and 3,760 km east of the coast of South America.
Pretty remote are the
Marquesas Islands (part of
French Polynesia). The archipelago is located in the South Pacific Ocean, 3,725 km southeast of
Hawaii. The nearest mainland is 5,000 km away at the southwestern coast of
Mexico; the second-nearest significant land is the east coast of
New Zealand, 5,230 km away.
Also in the middle of nowhere lies
Bouvet Island, or Bouvetøya. The uninhabited, glacier-covered, volcanic rock island is controlled by
Norway, which lies just 12,500 km to the north. The island is located in the chilly part of the South Atlantic Ocean, 2,530 km southwest off the tip of South Africa, 1,745 km north of the ice fields of Queen Maud Land, Antarctica, and 4,220 km east of Isla Grande de Tierra del Fuego, the island at the southern end of South America. Some consider Bouvet Island the most remote island in the world.
Largest Lakes The largest natural lakes on Earth by area are:
1.
Caspian Sea, 2. Lake Superior, 3. Lake Victoria, 4. Lake Huron, 5. Lake Michigan, 6. Lake Tanganyika, 7. Lake Baikal, 8. Great Bear Lake, 9. Lake Malawi (Lake Nyasa), 10. Great Slave Lake.
Major Rivers The top-five of the longest rivers on Earth are Nile (Africa), Amazon (South America), Yangtze (China), Mississippi (United States), and the Yenisey (Siberia, Russia).
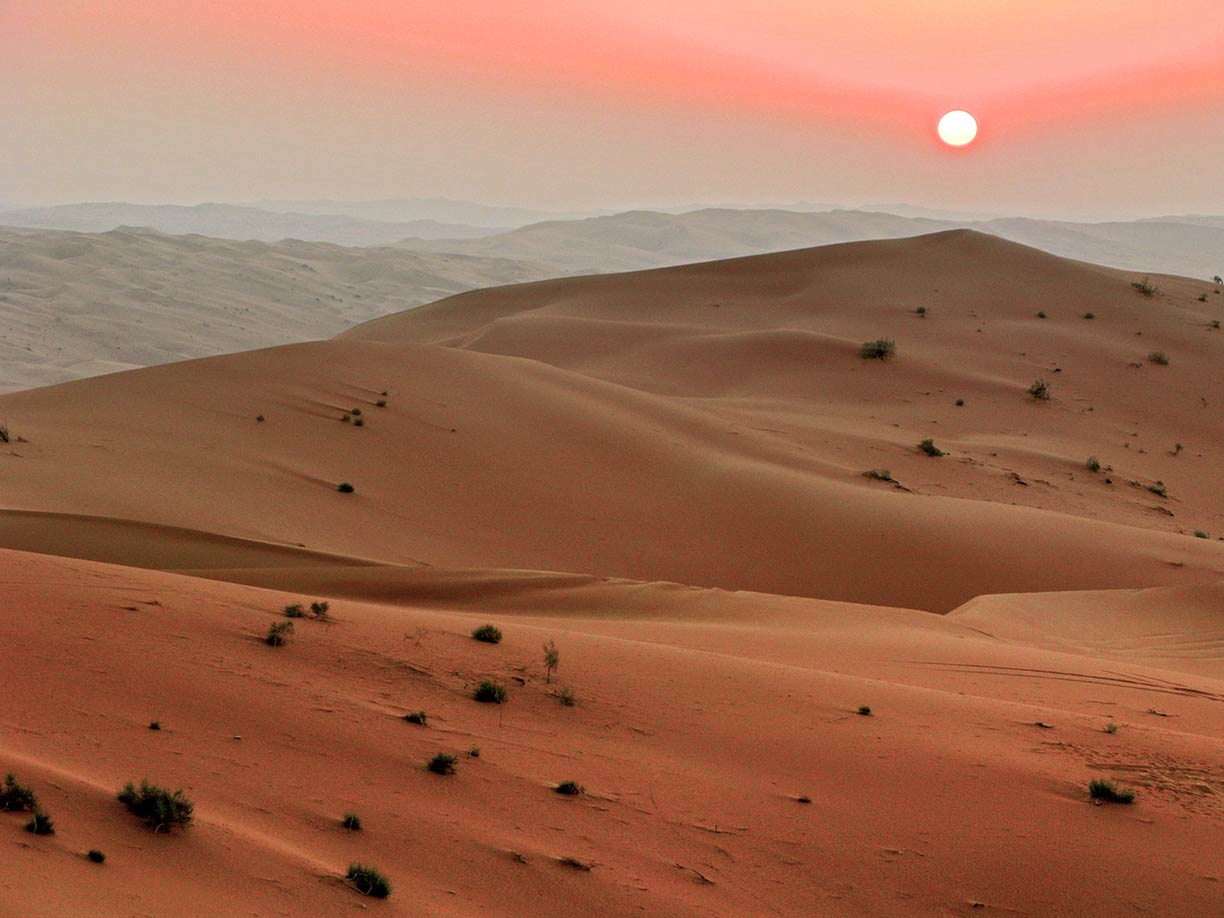 The image shows dunes in the Rub' al Khali, the Empty Quarter, in Saudi Arabia, a part of the Arabian Desert on the Arabian Peninsula. Image: Javierblas
The image shows dunes in the Rub' al Khali, the Empty Quarter, in Saudi Arabia, a part of the Arabian Desert on the Arabian Peninsula. Image: Javierblas By far the largest desert is
Antarctica with 14.2 million km², followed by the Arctic region located at the northernmost part of Earth. Both are polar deserts, also known as ice deserts, zones of the Earth, which feature an ice cap climate (arid and very cold).
Large parts of
Greenland are also considered a desert, an area without or with little vegetation. By the way, Greenland is the country with the lowest population density, and no, it is not for sale.
The largest "real" or true desert is the
Sahara. The arid subtropical area of land extends over 9.2 million km² and covers most of North Africa; it is the world's largest hot desert.
The
Sahel to the south of the Sahara is the biogeographical semi-arid transition zone
between the desert to the north and the Sudanian savanna to the south.
Next in size are the various
Deserts of Australia, which cover nearly 1.4 million km², about 18% of Australia's mainland territory. Apart from the polar regions, Australia is the driest continent in the world. About 35 percent of the continent receives so little rain that it is basically a desert.
The
Arabian Desert (2.3 million km²) covers most of the
Arabian Peninsula, situated between the Red Sea and the Persian Gulf.
The
Gobi Desert to the east of the
Taklamakan Desert covers parts of China's Inner Mongolia and southern parts of
Mongolia.
The
Kalahari Desert in southern Africa is a big, subtropical, semi-arid sandy savannah extending for 900,000 km².
Country facts The largest countries by
area are:
1.
Russia (17,098,242 km²), 2.
Canada (9,984,670 km²), 3.
United States (9,833,517 km²)
The
most populous countries in the world are (in 2020):
1.
China (1.44 billion), 2.
India (1.38 billion), 3.
United States (330,125,000), 4.
Indonesia (271,066,000), 5.
Pakistan (220,892,000)