
 |
|
Map of the Caspian Sea with surrounding Countries | |
About the Caspian Sea |
|
| Map is showing the Caspian Sea, an inland sea at the crossroads of Europe and Asia. The Caspian Sea is considered by many to be the largest lake in the world, lake or sea, it is the largest enclosed inland body of water on Earth with an area of 371,000 km² (without the Garabogazköl Bay), compared, the Caspian Sea is larger than Germany or somewhat smaller than the US state of Montana. The Caspian Sea is situated about 500 km east of the Black Sea, between southeastern Europe and Western Asia, east of the Caucasus Mountains, south of the vast Eurasian Steppe, and west of the Karakum and Kyzylkum Deserts of Central Asia. Five countries have a shoreline at the sea, Iran and four former Soviet republics (until 1991), Russia, Azerbaijan, Turkmenistan, and Kazakhstan, some of the world’s most repressive countries. The Caspian Sea lies within a land depression, it is actually the lowest natural point in Eurasia, the surface of the sea is about 21 m below mean sea level. The sea is completely isolated, there is no connection to other oceans. The main feeder is the Volga River (80% of the Caspian's inflow), other inflows are the Ural River, the Kura, and the Terek River. There is no discharge by any river, water leaves the sea only by evaporation. The Caspian Sea is known as the source for Beluga Caviar, which comes from the critically endangered beluga sturgeon. The sea is also known for its abundance of energy resources (oil and natural gas reserves in offshore fields and onshore on the coast of the sea), all states at the Caspian exploit the reserves in cooperation with international oil companies. But much of the offshore oil and natural gas resources in the Caspian Sea have not been tapped, as there are conflicts between the five bordering states over where to demarcate the maritime borders and how to split up the energy resources. Depicted on the map are the countries and regions surrounding the Caspian Sea, with international borders and major cities. |
Bookmark/share this page 
|
 One World - Nations Online countries of the world |
|
|
||
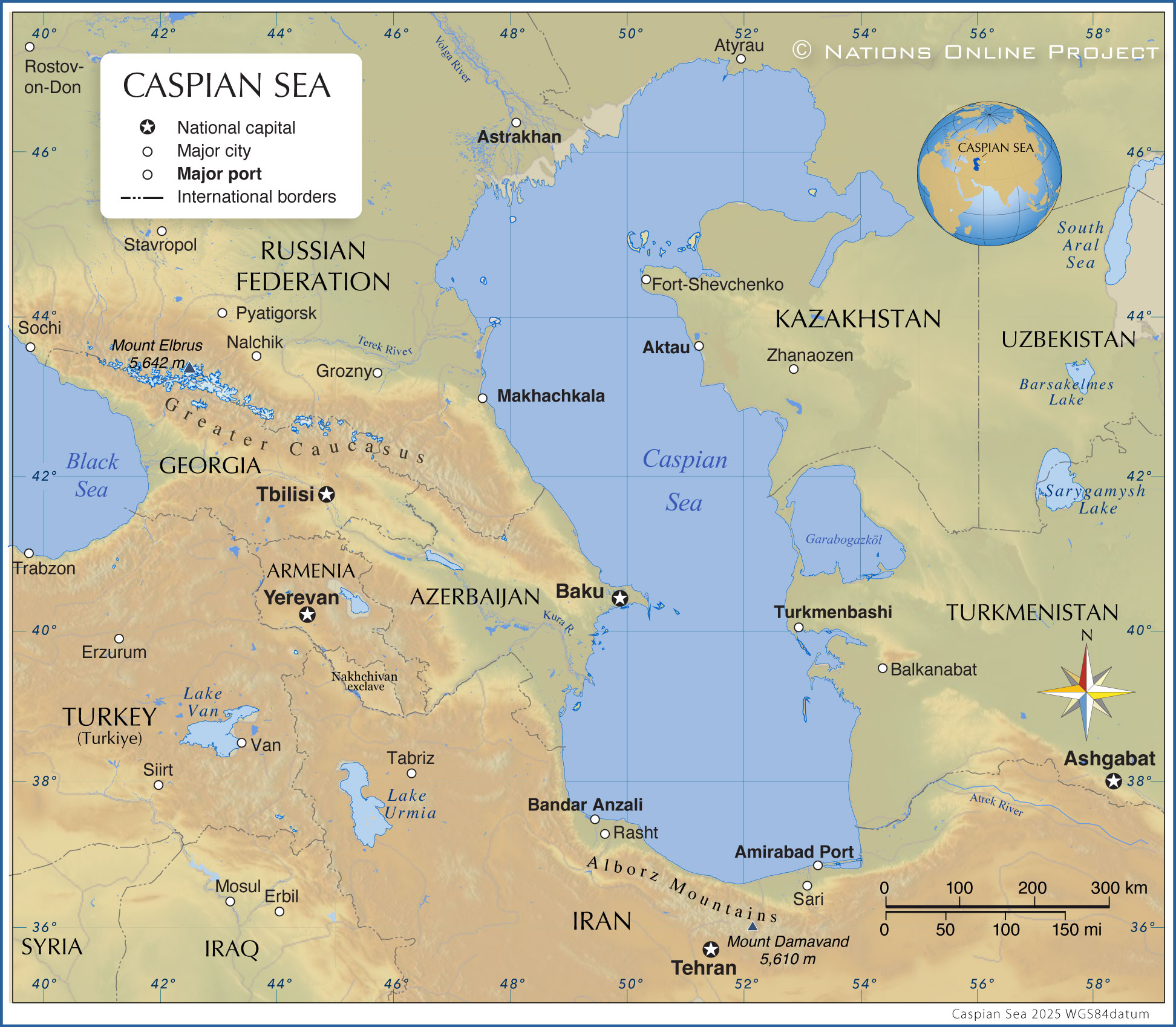 Map of the Caspian Sea |
|||||||||||
| Related Maps: |
Tehran Current Weather Conditions |
Baku Current Weather Conditions |
Related Consumer Information: |
||||||||
One World - Nations Online .:. let's care for this planet Every nation is responsible for the current state of our world. |
| Site Map
| Information Sources | Disclaimer: Privacy Policy, etc. Contact: [email protected] | Copyright © 1998-2021 :: nationsonline.org |